Molecular docking, dynamics and in vitro analysis of multi-target inhibitors for Clostridioides difficile
- PMID: 38352908
- PMCID: PMC10859948
- DOI: 10.6026/973206300200039
Molecular docking, dynamics and in vitro analysis of multi-target inhibitors for Clostridioides difficile
Abstract
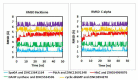
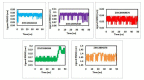
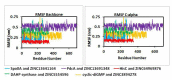
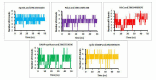
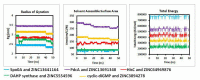
The opportunistic pathogen, Clostridioides difficile owes its extreme pathogenicity for its ability to develop antibiotic resistance and recurrent infections. The current antibiotics used for the treatment are showing declining sensitivity and rising antibiotic resistance. Therefore, it is of interest to develop the anti-clostridial drugs to overcome these issues. Hence, we have explored ZINC library to find the suitable lead compounds against five target proteins of C. difficile. Multistep virtual screening is performed to find the suitable compounds that are checked for their stability using molecular dynamics and are validated in vitro against C. difficile. In our study, five compounds viz., ZINC64969876, ZINC13641164, ZINC13691348, ZINC5554596 and ZINC3894278 that inhibit HisC, Spo0A, PdcA, DAHP synthase and cyclic-di GMP proteins, respectively have been identified. Further, these compounds were tested in vitro against four different isolates of C. difficile and all of them were found to inhibit the pathogen. However, to use these compounds as anti-clostridial drugs, further testing needs to be done. The selected compounds from our study are reported for the first time as antimicrobial agents against C. difficile.
Keywords: Clostridioides difficile; compounds; dynamics; in silico; in vitro; inhibition; molecular docking; pathogen.
© 2024 Biomedical Informatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
