Sensing Dying Cells in Health and Disease: The Importance of Kidney Injury Molecule-1
- PMID: 38353655
- PMCID: PMC11164124
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000334
Sensing Dying Cells in Health and Disease: The Importance of Kidney Injury Molecule-1
Abstract
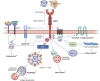
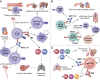
Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), also known as T-cell Ig and mucin domain-1 (TIM-1), is a widely recognized biomarker for AKI, but its biological function is less appreciated. KIM-1/TIM-1 belongs to the T-cell Ig and mucin domain family of conserved transmembrane proteins, which bear the characteristic six-cysteine Ig-like variable domain. The latter enables binding of KIM-1/TIM-1 to its natural ligand, phosphatidylserine, expressed on the surface of apoptotic cells and necrotic cells. KIM-1/TIM-1 is expressed in a variety of tissues and plays fundamental roles in regulating sterile inflammation and adaptive immune responses. In the kidney, KIM-1 is upregulated on injured renal proximal tubule cells, which transforms them into phagocytes for clearance of dying cells and helps to dampen sterile inflammation. TIM-1, expressed in T cells, B cells, and natural killer T cells, is essential for cell activation and immune regulatory functions in the host. Functional polymorphisms in the gene for KIM-1/TIM-1, HAVCR1 , have been associated with susceptibility to immunoinflammatory conditions and hepatitis A virus-induced liver failure, which is thought to be due to a differential ability of KIM-1/TIM-1 variants to bind phosphatidylserine. This review will summarize the role of KIM-1/TIM-1 in health and disease and its potential clinical applications as a biomarker and therapeutic target in humans.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
J.D. Dikeakos reports research funding from AffinityImmuno, a patent pending related to AffinityImmuno, and an advisory or leadership role for Canadian Society for Virology (Board of Directors). L. Gunaratnam reports advisory roles for and honoraria from Alexion, AstraZeneca Canada Inc., Bayer, GSK, Merck, Novartis Canada Inc., and Paladin Labs Inc.; advisory or leadership roles for Alexion, AstraZeneca Canada Inc., GSK, Merck, Novartis Canada Inc., and Paladin Labs Inc.; ownership interest in Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. (MRTX); and other advisory or leadership for Canadian Blood Services, Canadian Society of Transplantation, Kidney Foundation of Canada, Ontario Medical Association, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Trillium Gift of Life Network. R.S. Suri reports honoraria from Amgen, Bayer, and Otsuka and advisory or leadership roles for Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health, Canadian Society of Nephrology, and McGill University. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

