Guidance for use of neurofilament light chain as a cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarker in multiple sclerosis management
- PMID: 38354532
- PMCID: PMC10875256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.104970
Guidance for use of neurofilament light chain as a cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarker in multiple sclerosis management
Abstract
Neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a long-awaited blood biomarker that can provide clinically useful information about prognosis and therapeutic efficacy in multiple sclerosis (MS). There is now substantial evidence for this biomarker to be used alongside magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and clinical measures of disease progression as a decision-making tool for the management of patients with MS. Serum NfL (sNfL) has certain advantages over traditional measures of MS disease progression such as MRI because it is relatively noninvasive, inexpensive, and can be repeated frequently to monitor activity and treatment efficacy. sNfL levels can be monitored regularly in patients with MS to determine change from baseline and predict subclinical disease activity, relapse risk, and the development of gadolinium-enhancing (Gd+) lesions. sNfL does not replace MRI, which provides information related to spatial localisation and lesion stage. Laboratory platforms are starting to be made available for clinical application of sNfL in several countries. Further work is needed to resolve issues around comparisons across testing platforms (absolute values) and normalisation (reference ranges) in order to guide interpretation of the results.
Keywords: Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers; Multiple sclerosis; Neurofilament light chain; Serum biomarkers.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests MSF- Receipt of research or educational grants: Sanofi-Genzyme Canada. Receipt of honoraria or consultation fees: Alexion/Astra Zeneca, BiogenIdec, EMD Inc./EMD Serono/Merck Serono, Find Therapeutics, Hoffman La-Roche, Horizon Therapeutics, Novartis, Sandoz, Sanofi-Genzyme, Teva Canada Innovation. Member of a company advisory board, board of directors or other similar group: Alexion/Astra Zeneca, Actelion/Janssen (J&J), Atara Biotherapeutics, Bayer Healthcare, Celestra Health, EMD Inc./Merck Serono, Find Therapeutics, Hoffman La-Roche, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Setpoint Medical. Participation in a company sponsored speaker’s bureau: Hoffman La-Roche, Novartis, EMD Inc. SG-Grants or contracts: Sanofi-Genzyme, Merck, Takeda, UK MS Society, NMSS, NIHR, NHS Digital. Consulting fees: Merck, Sanofi-Genzyme, Novartis, Biogen Idec, Roche. Payment or honoraria: MS Academy, MS Research Australia, UK MS Society, CMSC, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Merck, TriMS, Janssen, Neurodiem, MS Shift. Support for meetings: Novarti, Merck, Sanofi-Genzyme, Biogen Idec. Leadership or fiduciary role: UK PD and MS Society Brain Bank. RAB-Payment or Honoraria: Roche. Support for attending meetings: CMSC. Participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board: Siemens. PAC-Royalties or Licences: Cambridge Press. Consulting fees: Novartis, Idorsia, Lilly. Support for meeting attendance: European Charcot Foundation. Patents planned, issued or pending: Methods, compositions, and kits for treating MS and other disorders. Participation on a data safety monitoring board: Vaccitech. Leadership or fiduciary role: NAIMS Board, IMS Visual, NMSS clinical trials comm. Stock or stock options: Vaccitech, Disarm. Receipt of equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts or other services: LABP66, research compound from Landos Bio. MK-Grants or contracts: Biogen, Novartis. Consulting fees: Biogen, Merck, Roche, Novartis, Bristol-Myers-Squibb and Gilean. JK- Speaker fees, research support, travel support, and/or served on advisory boards: Swiss MS Society, Swiss National Research Foundation (320030_189140/1), University of Basel, Progressive MS Alliance, Alnylam, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Immunic, Merck, Neurogenesis, Novartis, Octave Bioscience, Quanterix, Roche, Sanofi, Stata DX. JL- Advisory board: Amgen, Almirall, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi and Sandoz; Lecture honoraria: Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Sanofi; Safety Monitoring Board: GE Neuro; Chair: Board for MS therapies associated to the Swedish MS Association; Foundation of Swedish MS research. TO-Grants or contracts: Novartis, Biogen, Merck, Sanofi-Genzyme. Payment or honoraria: BiogenIdec, Merck, Novartis, Sandoz, Sanofi-Genzyme.
Figures
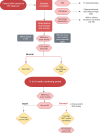
References
-
- Kuhle J., Plattner K., Bestwick J.P., et al. A comparative study of CSF neurofilament light and heavy chain protein in MS. Mult Scler. 2013;19(12):1597–1603. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Morillo E., Childs C., Garcia B.P., et al. Neurofilament medium polypeptide (NFM) protein concentration is increased in CSF and serum samples from patients with brain injury. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53(10):1575–1584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

