CDK4/6 inhibitors in lung cancer: current practice and future directions
- PMID: 38355149
- PMCID: PMC10865100
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0145-2023
CDK4/6 inhibitors in lung cancer: current practice and future directions
Abstract
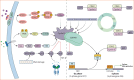
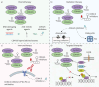
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and ∼85% of lung cancers are classified as nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These malignancies can proliferate indefinitely, in part due to dysregulation of the cell cycle and the resulting abnormal cell growth. The specific activation of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) is closely linked to tumour proliferation. Approximately 80% of human tumours exhibit abnormalities in the cyclin D-CDK4/6-INK4-RB pathway. Specifically, CDK4/6 inhibitors either as monotherapy or combination therapy have been investigated in pre-clinical and clinical studies for the treatment of NSCLC, and promising results have been achieved. This review article focuses on research regarding the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in NSCLC, including the characteristics and mechanisms of action of approved drugs and progress of pre-clinical and clinical research.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Research Progress of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 20;23(3):176-181. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.03.07. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32102134 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
A unique CDK4/6 inhibitor: Current and future therapeutic strategies of abemaciclib.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104686. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104686. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32068118 Review.
-
CDK4/6 inhibition synergizes with inhibition of P21-Activated Kinases (PAKs) in lung cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 17;16(6):e0252927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252927. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34138895 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antitumor properties of a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, P276-00.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):918-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0613. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17363486
-
Down-regulation of RCC1 sensitizes immunotherapy by up-regulating PD-L1 via p27kip1 /CDK4 axis in non-small cell lung cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Apr;25(8):4136-4147. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16383. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33630417 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting CDK4/6 suppresses colorectal cancer by destabilizing YAP1.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 17;6(3):e70103. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70103. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39968498 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of CDK4/6 inhibitors in tumor immunity and the potential value of tumor immunotherapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Aug;56(2):123. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5564. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40511560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in Targeting the Cell Cycle in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;17(8):1291. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081291. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small cell lung cancer: emerging subtypes, signaling pathways, and therapeutic vulnerabilities.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;13(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00548-w. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39103941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota as a biomarker and modulator of anti-tumor immunotherapy outcomes.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 28;15:1471273. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1471273. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39669573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
