Intrahepatic Transcriptomics Differentiate Advanced Fibrosis and Clinical Outcomes in Adults With Fontan Circulation
- PMID: 38355242
- PMCID: PMC11627240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.12.005
Intrahepatic Transcriptomics Differentiate Advanced Fibrosis and Clinical Outcomes in Adults With Fontan Circulation
Abstract
Background: The molecular mechanisms underlying Fontan-associated liver disease (FALD) remain largely unknown.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess intrahepatic transcriptomic differences among patients with FALD according to the degree of liver fibrosis and clinical outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included adults with the Fontan circulation. Baseline clinical, laboratory, imaging, and hemodynamic data as well as a composite clinical outcome (CCO) were extracted from medical records. Patients were classified into early or advanced fibrosis. RNA was isolated from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded liver biopsy samples; RNA libraries were constructed with the use of an rRNA depletion method and sequenced on an Illumina Novaseq 6000. Differential gene expression and gene ontology analyses were performed with the use of DESeq2 and Metascape.
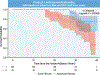
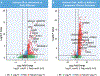
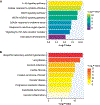
Results: A total of 106 patients (48% male, median age 31 years [IQR: 11.3 years]) were included. Those with advanced fibrosis had higher B-type natriuretic peptide levels and Fontan, mean pulmonary artery, and capillary wedge pressures. The CCO was present in 23 patients (22%) and was not predicted by advanced liver fibrosis, right ventricular morphology, presence of aortopulmonary collaterals, or Fontan pressures on multivariable analysis. Samples with advanced fibrosis had 228 upregulated genes compared with early fibrosis. Samples with the CCO had 894 upregulated genes compared with those without the CCO. A total of 136 upregulated genes were identified in both comparisons and were enriched in cellular response to cytokine stimulus or oxidative stress, VEGFA-VEGFR2 signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway, and vasculature development.
Conclusions: Patients with FALD and advanced fibrosis or the CCO exhibited upregulated genes related to inflammation, congestion, and angiogenesis.
Keywords: Fontan outcomes; Fontan-associated liver disease; liver fibrosis; single ventricle; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2024 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures Dr Bravo-Jaimes was supported by the Adult Congenital Heart Association Research Grant 2021. Dr Klomhaus was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Center for Advancing Translational Science UCLA CTSI grant no. UL1TR001881. Dr Böstrom was supported by NIH/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant nos. HL81397 and HL154548. Dr Aboulhosn was supported by the Streisand/American Heart Association Endowed Chair in Cardiology. Dr Kaldas was supported by the Kelly Lee Tarantello Endowed Chair in Integrative Liver Transplantation. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures



Update of
-
Intrahepatic transcriptomics differentiate advanced fibrosis and clinical outcomes in adults with the Fontan circulation.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 7:2023.06.05.23290997. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.05.23290997. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Feb 20;83(7):726-738. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.12.005. PMID: 37333414 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Turning to "Omics" in Understanding Fontan-Associated Liver Disease.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024 Feb 20;83(7):739-740. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.12.025. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38355243 No abstract available.

