Recent advances of m6A methylation in skeletal system disease
- PMID: 38355483
- PMCID: PMC10868056
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-04944-y
Recent advances of m6A methylation in skeletal system disease
Abstract
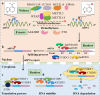
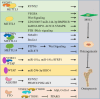
Skeletal system disease (SSD) is defined as a class of chronic disorders of skeletal system with poor prognosis and causes heavy economic burden. m6A, methylation at the N6 position of adenosine in RNA, is a reversible and dynamic modification in posttranscriptional mRNA. Evidences suggest that m6A modifications play a crucial role in regulating biological processes of all kinds of diseases, such as malignancy. Recently studies have revealed that as the most abundant epigentic modification, m6A is involved in the progression of SSD. However, the function of m6A modification in SSD is not fully illustrated. Therefore, make clear the relationship between m6A modification and SSD pathogenesis might provide novel sights for prevention and targeted treatment of SSD. This article will summarize the recent advances of m6A regulation in the biological processes of SSD, including osteoporosis, osteosarcoma, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, and discuss the potential clinical value, research challenge and future prospect of m6A modification in SSD.
Keywords: Osteoarthritis; Osteoporosis; Osteosarcoma; Rheumatoid arthritis; m6A modification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

