Performance of ChatGPT on Chinese national medical licensing examinations: a five-year examination evaluation study for physicians, pharmacists and nurses
- PMID: 38355517
- PMCID: PMC10868058
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-05125-7
Performance of ChatGPT on Chinese national medical licensing examinations: a five-year examination evaluation study for physicians, pharmacists and nurses
Abstract
Background: Large language models like ChatGPT have revolutionized the field of natural language processing with their capability to comprehend and generate textual content, showing great potential to play a role in medical education. This study aimed to quantitatively evaluate and comprehensively analysis the performance of ChatGPT on three types of national medical examinations in China, including National Medical Licensing Examination (NMLE), National Pharmacist Licensing Examination (NPLE), and National Nurse Licensing Examination (NNLE).
Methods: We collected questions from Chinese NMLE, NPLE and NNLE from year 2017 to 2021. In NMLE and NPLE, each exam consists of 4 units, while in NNLE, each exam consists of 2 units. The questions with figures, tables or chemical structure were manually identified and excluded by clinician. We applied direct instruction strategy via multiple prompts to force ChatGPT to generate the clear answer with the capability to distinguish between single-choice and multiple-choice questions.
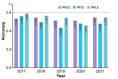
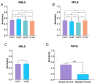
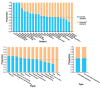
Results: ChatGPT failed to pass the accuracy threshold of 0.6 in any of the three types of examinations over the five years. Specifically, in the NMLE, the highest recorded accuracy was 0.5467, which was attained in both 2018 and 2021. In the NPLE, the highest accuracy was 0.5599 in 2017. In the NNLE, the most impressive result was shown in 2017, with an accuracy of 0.5897, which is also the highest accuracy in our entire evaluation. ChatGPT's performance showed no significant difference in different units, but significant difference in different question types. ChatGPT performed well in a range of subject areas, including clinical epidemiology, human parasitology, and dermatology, as well as in various medical topics such as molecules, health management and prevention, diagnosis and screening.
Conclusions: These results indicate ChatGPT failed the NMLE, NPLE and NNLE in China, spanning from year 2017 to 2021. but show great potential of large language models in medical education. In the future high-quality medical data will be required to improve the performance.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; ChatGPT; Medical education; Medical examination; Natural language processing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bhinder B, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Research and Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(4):900–15. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0090. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sarink MJ et al. A study on the performance of ChatGPT in infectious diseases clinical consultation. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2023. - PubMed
-
- Lee TC et al. ChatGPT Answers Common Patient Questions About Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology, 2023. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

