Cost-consequence analysis of tocilizumab versus adalimumab and etanercept among rheumatoid arthritis patients in Saudi Arabia: a single-center study
- PMID: 38355532
- PMCID: PMC10868060
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-024-00522-7
Cost-consequence analysis of tocilizumab versus adalimumab and etanercept among rheumatoid arthritis patients in Saudi Arabia: a single-center study
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to examine the direct medical cost and impact of tocilizumab (TOZ) versus adalimumab (ADM) and etanercept (ETC) on reducing the levels of two inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)) among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using real-world data from Saudi Arabia.
Method: This was a single-center retrospective cohort study in which data for biologic-naïve RA patients aged ≥ 18 years and treated with TOZ, ADM, ETC were retrieved from the electronic medical records (EMRs) of a university-affiliated tertiary care center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Patients were followed up at least one year after the treatment initiation. Bottom-up microcosting was utilized to estimate the direct medical costs. Additionally, inverse probability treatment weighting and bootstrapping with 10,000 replications were conducted to generate 95% confidence levels for costs and the mean reductions in CRP and ESR levels.
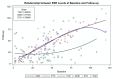
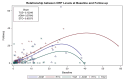
Results: The number of patients who met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis was 150 patients (TOZ (n = 56), ADM (n = 41), ETC (n = 53)). Patients on TOZ had 3.96 mg/L (95% CI: -0.229-4.95) and 11.21 mm/hr (95% CI: 10.28-18.11) higher mean reductions in the CRP and ESR levels compared to their counterparts on ADM, ETC, respectively. However, this was associated with mean annual incremental costs of USD 10,087.88 (95% CI: 9494.50-11,441.63) in all cost-effectiveness bootstrap distributions.
Conclusion: Tocilizumab has shown better effectiveness in reducing the levels of CRP and ESR but with higher costs. Future studies should examine whether the reduction of these two inflammatory markers is associated with quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gains.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Arthritis; Cost analysis; Etanercept; Rheumatoid; Tocilizumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life of patients with rheumatoid arthritis on tocilizumab, adalimumab, and etanercept in Saudi Arabia: a single-center cross-sectional study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1299630. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1299630. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38161694 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of upadacitinib as a treatment option for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.J Med Econ. 2024 Jan-Dec;27(1):134-144. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2299176. Epub 2024 Jan 1. J Med Econ. 2024. PMID: 38163926
-
Cost-effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept, and tocilizumab as first-line treatments for moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis.J Med Econ. 2012;15(2):340-51. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2011.649327. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Med Econ. 2012. PMID: 22168785
-
Effectiveness and Costs Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Targeted Immunomodulators Using Real-World U.S. Data.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020 Aug;26(8):1039-1049. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2020.26.8.1039. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32715967 Free PMC article.
-
Review of eight pharmacoeconomic studies of the value of biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Sep;12(7):555-69. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.7.555. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16981801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Balancing the Scales: The Dual Role of Interleukins in Bone Metastatic Microenvironments.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8163. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158163. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

