EURO-NMD registry: federated FAIR infrastructure, innovative technologies and concepts of a patient-centred registry for rare neuromuscular disorders
- PMID: 38355534
- PMCID: PMC10865673
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-024-03059-3
EURO-NMD registry: federated FAIR infrastructure, innovative technologies and concepts of a patient-centred registry for rare neuromuscular disorders
Abstract
Background: The EURO-NMD Registry collects data from all neuromuscular patients seen at EURO-NMD's expert centres. In-kind contributions from three patient organisations have ensured that the registry is patient-centred, meaningful, and impactful. The consenting process covers other uses, such as research, cohort finding and trial readiness.
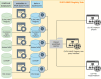
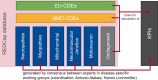
Results: The registry has three-layered datasets, with European Commission-mandated data elements (EU-CDEs), a set of cross-neuromuscular data elements (NMD-CDEs) and a dataset of disease-specific data elements that function modularly (DS-DEs). The registry captures clinical, neuromuscular imaging, neuromuscular histopathology, biological and genetic data and patient-reported outcomes in a computer-interpretable format using selected ontologies and classifications. The EURO-NMD registry is connected to the EURO-NMD Registry Hub through an interoperability layer. The Hub provides an entry point to other neuromuscular registries that follow the FAIR data stewardship principles and enable GDPR-compliant information exchange. Four national or disease-specific patient registries are interoperable with the EURO-NMD Registry, allowing for federated analysis across these different resources.
Conclusions: Collectively, the Registry Hub brings together data that are currently siloed and fragmented to improve healthcare and advance research for neuromuscular diseases.
Keywords: FAIR data; Neuromuscular Diseases; Rare Diseases; Registry; Registry Hub.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Adrian Tassoni, Antonio Atalaia, Carla D’Angelo, Catherine Eng, Dagmar Wandrei, Dalil Hamroun, Dimitrios Athanasiou, Elizabeth Vroom, Esther Brusse, Evy Reviers, François Lamy, Georgios Paliouras, Hadrien Delattre, Jean-Philippe Plançon, Laura Blacas, Maxime Jacoupy, Michelangelo Mancuso, Nawel Lalout, Paraskevi Sakellariou, Peter-Bram ’t Hoen, Rachel Thompson, Rita Horvath, Suzie-Ann Baker, Teresinha Evangelista declared no conflicts of interest. Antonio Toscano: Reimbursements for participation to scientific boards and for educational activities from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, Astellas, Bayer, Aro and Spark. Carmen Paradas: Advisory Board honoraria from UCB, Alexion, Sanofi-Genzyme. Cornelia Kornblum: Travel funding and/or speaker honoraria from Chiesi, Amicus Therapeutics, Fulcrum Therapeutics, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme, Santhera and acknowledges financial support as advisory board member and/or primary investigator for Amicus Therapeutics, Fulcrum Therapeutics, Hormosan, Reneo Pharmaceuticals, Roche Pharma AG, Sanofi Genzyme, Stealth BioTherapeutics. Davide Pareyson: Financial support from Alnylam and Kedrion for participation in international meetings, participation in Advisory Boards of Inflectis, Alnylam, Akcea, Arvinas, Augustine Tx, DTx, speaker honorarium from Alnylam. Guillaume Bassez: Research funding from AFM-Telethon and compensation for consulting services and/or speaking activities from Biogen, Dyne therapeutics, Lupin Pharmaceutical. Hanns Lochmuller: Support from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Foundation Grant FDN-167281), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Muscular Dystrophy Canada (Network Catalyst Grant for NMD4C), the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI-JELF 38412), and the Canada Research Chairs program (Canada Research Chair in Neuromuscular Genomics and Health, 950–232279). Jana Haberlova: Honoraria as a advisory board members or speaker for Roche,Novartis, Biogen, PTC. Janbernd Kirschner: Consultancy and/or speaker honoraria from Biogen, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche and research grants from Biogen, Novartis, Roche. Janneke G. J. Hoeijmakers: Grants from the Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds (W.OK17-09 and W.TR22-01). Kristl G. Claeys: Speaker/Advisory board honoraria from Alexion, Alnylam, Amicus, ArgenX, Biogen, CSL Behring, Ipsen, Janssen Pharmaceutics, Lupin, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, UCB; and Research funding from CSL Behring (Chair), Alnylam, Biogen, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme. Marianne de Visser: Consultancy honoraria from Novartis and Argenx. Mark D Wilkinson: Co-Founder of FAIR Data Systems S.L., Madrid, who were contracted to do some portions of the work with several of the registries described in this paper. Melinda Gyenge: Research funding from AFM-Telethon. Nadine van der Beek: Advisory boards of Sanofi, and Amicus Therapeutics. She received speaker honoraria Sanofi. Vincenzo Silani: Compensation for consulting services and/or speaking activities from AveXis, Cytokinetics, Italfarmaco, Liquidweb S.r.l., Novartis Pharma AG and Zambon. He receives or has received research supports form the Italian Ministry of Health, AriSLA, and E-Rare Joint Transnational Call. He is in the Editorial Board of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration, European Neurology, American Journal of Neurodegenerative Diseases, Frontiers in Neurology, and Exploration of Neuroprotective Therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Parliament E. Directive 2011/24/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 9 March 2011 on the application of patients' rights in cross-border healthcare, 2011. CELEX: EC. Available: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32011L0024... [Accessed 19/04/2022 2022].
-
- Austin CP, Cutillo CM, Lau LPL, Jonker AH, Rath A, Julkowska D, Thomson D, Terry S. F, de Montleau B, Ardigo D, Hivert V, Boycott KM, Baynam G, Kaufmann P, Taruscio D, Lochmuller H, Suematsu M, Incerti C, Draghia-Akli R, Norstedt I, Wang L, Dawkins HJS, International Rare Diseases Research C, Future of rare diseases research 2017–2027: an IRDiRC perspective. Clin Transl Sci. 2018;, 11:21–27 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical