The use of synaptic biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid to differentiate behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia from primary psychiatric disorders and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38355535
- PMCID: PMC10865562
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01409-8
The use of synaptic biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid to differentiate behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia from primary psychiatric disorders and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Lack of early molecular biomarkers in sporadic behavioral variants of frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) and its clinical overlap with primary psychiatric disorders (PPD) hampers its diagnostic distinction. Synaptic dysfunction is an early feature in bvFTD and identification of specific biomarkers might improve its diagnostic accuracy. Our goal was to understand the differential diagnostic potential of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) synaptic biomarkers in bvFTD versus PPD and their specificity towards bvFTD compared with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and controls. Additionally, we explored the association of CSF synaptic biomarkers with social cognition, cognitive performance, and disease severity in these clinical groups.
Methods: Participants with probable bvFTD (n = 57), PPD (n = 71), AD (n = 60), and cognitively normal controls (n = 39) with available CSF, cognitive tests, and disease severity as frontotemporal lobar degeneration-modified clinical dementia rating scale (FTLD-CDR) were included. In a subset of bvFTD and PPD cases, Ekman 60 faces test scores for social cognition were available. CSF synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP25), neurogranin (Ng), neuronal pentraxin 2 (NPTX2), and glutamate receptor 4 (GluR4) were measured, along with neurofilament light (NfL), and compared between groups using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) and logistic regression. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed using ROC analyses, and biomarker panels were selected using Wald's backward selection. Correlations with cognitive measures were performed using Pearson's partial correlation analysis.
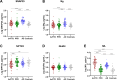
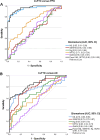
Results: NPTX2 concentrations were lower in the bvFTD group compared with PPD (p < 0.001) and controls (p = 0.003) but not compared with AD. Concentrations of SNAP25 (p < 0.001) and Ng (p < 0.001) were elevated in patients with AD versus those with bvFTD and controls. The modeled panel for differential diagnosis of bvFTD versus PPD consisted of NfL and NPTX2 (AUC = 0.96, CI: 0.93-0.99, p < 0.001). In bvFTD versus AD, the modeled panel consisted of NfL, SNAP25, Ng, and GluR4 (AUC = 0.86, CI: 0.79-0.92, p < 0.001). In bvFTD, lower NPTX2 (Pearson's r = 0.29, p = 0.036) and GluR4 (Pearson's r = 0.34, p = 0.014) concentrations were weakly associated with worse performance of total cognitive score. Lower GluR4 concentrations were also associated with worse MMSE scores (Pearson's r = 0.41, p = 0.002) as well as with worse executive functioning (Pearson's r = 0.36, p = 0.011) in bvFTD. There were no associations between synaptic markers and social cognition or disease severity in bvFTD.
Conclusion: Our findings of involvement of NTPX2 in bvFTD but not PPD contribute towards better understanding of bvFTD disease pathology.
Keywords: Differential diagnosis; Frontotemporal dementia; Primary psychiatric disorders; Synaptic biomarkers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.D., and J.G., are employees of ADx NeuroSciences, Gent, Belgium. E.V. is the co-founder of ADx NeuroSciences. D.J. is a former employee of ADx NeuroSciences, Gent, Belgium, and is recently retired. C.E.T. has a collaboration contract with ADx NeuroSciences, Quanterix, and Eli Lilly, and has performed contract research or received grants from AC-Immune, Axon Neurosciences, Bioconnect, Bioorchestra, Brainstorm Therapeutics, Celgene, EIP Pharma, Eisai, Grifols, Novo Nordisk, PeopleBio, Roche, Toyama, and Vivoryon. She serves on editorial boards of Medidact Neurologie/Springer, Alzheimer Research and Therapy, Neurology: Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, and is the editor of a Neuromethods book Springer. All the other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Woolley JD, Khan BK, Murthy NK, Miller BL, Rankin KP. The diagnostic challenge of psychiatric symptoms in neurodegenerative disease; rates of and risk factors for prior psychiatric diagnosis in patients with early neurodegenerative disease. The Journal of clinical psychiatry. 2011;72(2):126. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10m06382oli. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vijverberg EG, Wattjes MP, Dols A, Krudop WA, Möller C, Peters A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI and additional [18F] FDG-PET for behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia in patients with late onset behavioral changes. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2016;53(4):1287–97. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160285. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 860197/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation Marie Curie program 'MIRIADE'
- 860197/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation Marie Curie program 'MIRIADE'
- 860197/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation Marie Curie program 'MIRIADE'
- #ZonMW 733050206/ZonMW-funded PRODIA project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

