Cai's prescription inhibits granulosa cell apoptosis through ARHGAP4 on poor ovarian responders
- PMID: 38355537
- PMCID: PMC10865665
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-024-01363-x
Cai's prescription inhibits granulosa cell apoptosis through ARHGAP4 on poor ovarian responders
Abstract
Purpose: Poor ovarian response (POR) is a big challenge for in vitro fertilization. The traditional Chinese medicine, Cai's Prescription of Tonifying Kidney and Strengthening Vitals (Cai's Prescription) has yielded satisfactory results for POR treatment clinically, but systematic scientific research of Cai's Prescription is not well reported. This study aimed to investigate the clinical effect of Cai's Prescription on poor ovarian responders and its biological mechanism.
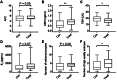
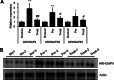
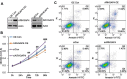
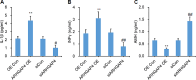
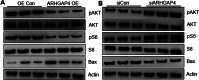
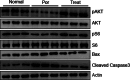
Methods: Serum was collected from poor ovarian responders, and IL-1β, INFγ, FSH, E2 and AMH levels were analyzed by ELISA. Ovarian antral follicles were identified and counted using transvaginal ultrasound. The embryo quality grading were done on day 3 after retrieval. We used high-throughput sequencing of granulosa cells to investigate the gene transcription patterns of ovarian granulosa cells in poor ovarian responders after Cai's Prescription pretreatment. The expression level of ARHGAP4 was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and western blot. The effects of ARHGAP4 for granulosa cells were analyzed by CCK-8 assay, annexin-V and PI staining, ELISA and western blot. The effects of Cai's Prescription on the expression of PI3K-Akt pathway and apoptosis were analyzed by western blot.
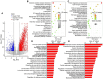
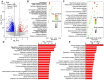
Results: In this study, we found that Cai's Prescription pretreatment had the tendency to improve the ovarian reserve function and could increase the number of high quality embryos for poor ovarian responders. Through high-throughput sequencing of mRNA in granulosa cells, we discovered ARHGAP4, which is a member of GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) may be a candidate target for POR treatment. ARHGAP4 was significantly increased in poor ovarian responders and can be recovered after Cai's Prescription pretreatment. Mechanically, combining the cell line model and clinical tissue samples, we found that ARHGAP4 can accelerate cell apoptosis and inflammation response in granulosa cells via PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. In addition, Cai's Prescription pretreatment for three months significantly reduced the high level of ARHGAP4 in poor ovarian responders.
Conclusion: This study shows that the traditional Chinese medicine, Cai's Prescription yielded satisfactory results for poor ovarian responders clinically and ARHGAP4 may be a candidate target for POR treatment.
Keywords: ARHGAP4; Apoptosis; Poor ovarian response; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of acupuncture at "Zhibian" (BL 54) through "Shuidao" (ST 28) on PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway in mice with poor ovarian response].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024 Jul 12;44(7):821-30. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230610-k0001. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38986596 Chinese.
-
Zihuai recipe alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced diminished ovarian reserve via suppressing PI3K/AKT-mediated apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Sep 15;277:113789. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113789. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33422655
-
[Qirong Tablets inhibits apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells via PI3K/Akt/ HIF-1 signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Sep;48(17):4774-4781. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230424.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802816 Chinese.
-
[Mechanism of protective effect of resveratrol on poor ovarian response in mice].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Nov;48(21):5888-5897. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230706.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114185 Chinese.
-
Cai's herbal tea enhances mitochondrial autophagy of type 1 diabetic mellitus β cells through the AMPK/mTOR pathway and alleviates inflammatory response.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Dec;61(12):1553-1567. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02316-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38954041 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

