Tanreqing injection inhibits dengue virus encephalitis by suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome
- PMID: 38355571
- PMCID: PMC10868054
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00893-2
Tanreqing injection inhibits dengue virus encephalitis by suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome
Abstract
Background: Encephalitis caused by dengue virus (DENV) is considered a manifestation of severe dengue. Tanreqing injection (TRQ) is a well-known Chinese patented medicine, which has been used to treat brain-related disorders by inhibiting inflammation. Nevertheless, the effects of TRQ on DENV encephalitis have not been studied. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of TRQ on DENV encephalitis and to explore its potential mechanisms.
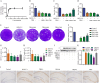
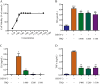
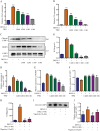
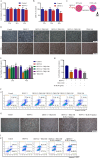
Methods: The cytotoxicity of TRQ was examined by MTT assay, and the anti-DENV activities of TRQ in BHK-21 baby hamster kidney fibroblast were evaluated through CCK-8 and plaque assays. The expression levels of NO, IL1B/IL-1β, TNFα and IL6 were measured by qRT‒PCR and ELISA in the BV2 murine microglial cell line. The inhibitory effects of TRQ on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in BV2 cells were examined by Western blotting, qRT‒PCR and ELISA. The effects of TRQ on HT22 mouse hippocampal neuronal cells were examined by CCK-8 assay, morphology observation and flow cytometry. Moreover, a DENV-infected ICR suckling mouse model was developed to investigate the protective role of TRQ in vivo.
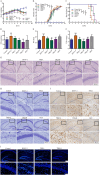
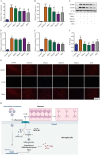
Results: TRQ decreased the release of NO, IL6, TNFα and IL1B from BV2 cells and inhibited the activation of NLRP3. The presence of the NLRP3 agonist nigericin reversed the anti-inflammatory activities of TRQ. Furthermore, TRQ inhibited the death of HT22 cells by decreasing IL1B in DENV-infected BV2 cells. In addition, TRQ significantly attenuated weight loss, reduced clinical scores and extended the survival in DENV-infected ICR suckling mice. Critically, TRQ ameliorated pathological changes in ICR suckling mice brain by inhibiting microglia and NLRP3 activation and decreasing the production of inflammatory factors and the number of dead neurons.
Conclusion: TRQ exerts potent inhibitory effects on dengue encephalitis in vitro and in vivo by reducing DENV-2-induced microglial activation and subsequently decreasing the inflammatory response, thereby protecting neurons. These findings demonstrate the potential of TRQ in the treatment of dengue encephalitis.
Keywords: Dengue; Encephalitis; NLRP3; Tanreqing injection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tanreqing injection demonstrates anti-dengue activity through the regulation of the NF-κB-ICAM-1/VCAM-1 axis.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul 25;130:155764. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155764. Epub 2024 May 19. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38797030
-
Dengue Virus M Protein Promotes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation To Induce Vascular Leakage in Mice.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00996-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00996-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31413130 Free PMC article.
-
Punicalagin Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation and ROS Production in Microglia by Inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 15;15:5347-5359. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S372773. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36131784 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an effective fraction from Ampelopsis Radix with anti-dengue virus activities in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;309:116339. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116339. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36870463
-
Inflammasome Fuels Dengue Severity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 10;10:489. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00489. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33014899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effect and Mechanism of Tanreqing Injection on Ischemic Stroke: Insights from Network Pharmacology and in vivo Experiments.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Aug;30(8):713-720. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3910-6. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38910191
-
Dengue and severe dengue with neurological complications: a challenge for prevention and control.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024 Dec;82(12):1-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1792091. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 39626875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

