In vitro induction of patterned branchial arch-like aggregate from human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 38355589
- PMCID: PMC10867012
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45285-0
In vitro induction of patterned branchial arch-like aggregate from human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
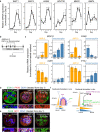
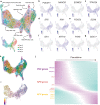
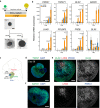
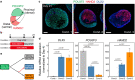
Early patterning of neural crest cells (NCCs) in the craniofacial primordium is important for subsequent development of proper craniofacial structures. However, because of the complexity of the environment of developing tissues, surveying the early specification and patterning of NCCs is difficult. In this study, we develop a simplified in vitro 3D model using human pluripotent stem cells to analyze the early stages of facial development. In this model, cranial NCC-like cells spontaneously differentiate from neural plate border-like cells into maxillary arch-like mesenchyme after a long-term culture. Upon the addition of EDN1 and BMP4, these aggregates are converted into a mandibular arch-like state. Furthermore, temporary treatment with EDN1 and BMP4 induces the formation of spatially separated domains expressing mandibular and maxillary arch markers within a single aggregate. These results suggest that this in vitro model is useful for determining the mechanisms underlying cell fate specification and patterning during early facial development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

