Epigenetic regulation of CD38/CD48 by KDM6A mediates NK cell response in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 38355622
- PMCID: PMC10866908
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45561-z
Epigenetic regulation of CD38/CD48 by KDM6A mediates NK cell response in multiple myeloma
Abstract
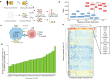
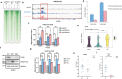
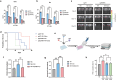
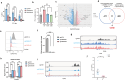
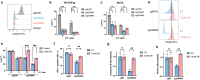
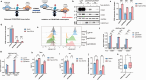
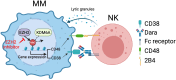
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies like Daratumumab (Dara) are effective in multiple myeloma (MM); however, drug resistance ultimately occurs and the mechanisms behind this are poorly understood. Here, we identify, via two in vitro genome-wide CRISPR screens probing Daratumumab resistance, KDM6A as an important regulator of sensitivity to Daratumumab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Loss of KDM6A leads to increased levels of H3K27me3 on the promoter of CD38, resulting in a marked downregulation in CD38 expression, which may cause resistance to Daratumumab-mediated ADCC. Re-introducing CD38 does not reverse Daratumumab-mediated ADCC fully, which suggests that additional KDM6A targets, including CD48 which is also downregulated upon KDM6A loss, contribute to Daratumumab-mediated ADCC. Inhibition of H3K27me3 with an EZH2 inhibitor resulted in CD38 and CD48 upregulation and restored sensitivity to Daratumumab. These findings suggest KDM6A loss as a mechanism of Daratumumab resistance and lay down the proof of principle for the therapeutic application of EZH2 inhibitors, one of which is already FDA-approved, in improving MM responsiveness to Daratumumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.C.A. serves on advisory boards to Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Starton, Window, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and is a Founder of OncoPep, C4 Therapeutics, Dynamic Cell Therapies, and NextRNA. All the other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

