HYDROchlorothiazide versus placebo to PROTECT polycystic kidney disease patients and improve their quality of life: study protocol and rationale for the HYDRO-PROTECT randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38355627
- PMCID: PMC10865620
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-024-07952-x
HYDROchlorothiazide versus placebo to PROTECT polycystic kidney disease patients and improve their quality of life: study protocol and rationale for the HYDRO-PROTECT randomized controlled trial
Abstract
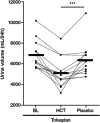
Background: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) leads to progressive renal cyst formation and loss of kidney function in most patients. Vasopressin 2 receptor antagonists (V2RA) like tolvaptan are currently the only available renoprotective agents for rapidly progressive ADPKD. However, aquaretic side effects substantially limit their tolerability and therapeutic potential. In a preliminary clinical study, the addition of hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) to tolvaptan decreased 24-h urinary volume and appeared to increase renoprotective efficacy. The HYDRO-PROTECT study will investigate the long-term effect of co-treatment with HCT on tolvaptan efficacy (rate of kidney function decline) and tolerability (aquaresis and quality of life) in patients with ADPKD.
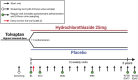
Methods: The HYDRO-PROTECT study is an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. The study is powered to enroll 300 rapidly progressive patients with ADPKD aged ≥ 18 years, with an eGFR of > 25 mL/min/1.73 m2, and on stable treatment with the highest tolerated dose of tolvaptan in routine clinical care. Patients will be randomly assigned (1:1) to daily oral HCT 25 mg or matching placebo treatment for 156 weeks, in addition to standard care.
Outcomes: The primary study outcome is the rate of kidney function decline (expressed as eGFR slope, in mL/min/1.73 m2 per year) in HCT versus placebo-treated patients, calculated by linear mixed model analysis using all available creatinine values from week 12 until the end of treatment. Secondary outcomes include changes in quality-of-life questionnaire scores (TIPS, ADPKD-UIS, EQ-5D-5L, SF-12) and changes in 24-h urine volume.
Conclusion: The HYDRO-PROTECT study will demonstrate whether co-treatment with HCT can improve the renoprotective efficacy and tolerability of tolvaptan in patients with ADPKD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
EM received consultancy fees from Otsuka and research funding from Sanofi and the Dutch Kidney Foundation. RG received consultancy fees and/or research grants from Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Galapagos, Ipsen, Mironid, Otsuka, and Sanofi. All money was paid to the institution. AP received research funding and lecture fees from Otsuka. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

