Author Correction: Zinc nanoparticles ameliorated obesity-induced cardiovascular disease: role of metabolic syndrome and iron overload
- PMID: 38355658
- PMCID: PMC10867024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-53947-8
Author Correction: Zinc nanoparticles ameliorated obesity-induced cardiovascular disease: role of metabolic syndrome and iron overload
Figures

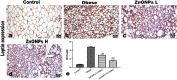
Erratum for
-
Zinc nanoparticles ameliorated obesity-induced cardiovascular disease: role of metabolic syndrome and iron overload.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 25;13(1):16010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42550-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37749096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Seidy AMA, Bashandy S, Ibrahim F, Abd El-Rahman S, Farid O, Moussa S, El-Baset M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles characterization and therapeutic evaluation on high fat/sucrose diet induced-obesity. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022;65(9):497–511. doi: 10.21608/ejchem.2022.112166.5113. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

