Nuclear morphology is shaped by loop-extrusion programs
- PMID: 38355805
- PMCID: PMC11052650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07086-9
Nuclear morphology is shaped by loop-extrusion programs
Abstract
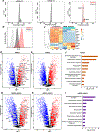
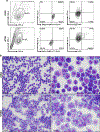
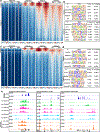
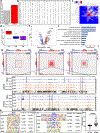
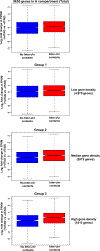
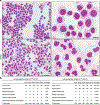
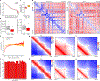
It is well established that neutrophils adopt malleable polymorphonuclear shapes to migrate through narrow interstitial tissue spaces1-3. However, how polymorphonuclear structures are assembled remains unknown4. Here we show that in neutrophil progenitors, halting loop extrusion-a motor-powered process that generates DNA loops by pulling in chromatin5-leads to the assembly of polymorphonuclear genomes. Specifically, we found that in mononuclear neutrophil progenitors, acute depletion of the loop-extrusion loading factor nipped-B-like protein (NIPBL) induced the assembly of horseshoe, banded, ringed and hypersegmented nuclear structures and led to a reduction in nuclear volume, mirroring what is observed during the differentiation of neutrophils. Depletion of NIPBL also induced cell-cycle arrest, activated a neutrophil-specific gene program and conditioned a loss of interactions across topologically associating domains to generate a chromatin architecture that resembled that of differentiated neutrophils. Removing NIPBL resulted in enrichment for mega-loops and interchromosomal hubs that contain genes associated with neutrophil-specific enhancer repertoires and an inflammatory gene program. On the basis of these observations, we propose that in neutrophil progenitors, loop-extrusion programs produce lineage-specific chromatin architectures that permit the packing of chromosomes into geometrically confined lobular structures. Our data also provide a blueprint for the assembly of polymorphonuclear structures, and point to the possibility of engineering de novo nuclear shapes to facilitate the migration of effector cells in densely populated tumorigenic environments.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 AG074591/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI102853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK107977/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA056006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG011585/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DA051411/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA051889/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HG011922/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DA047032/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R61 DA047032/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

