Intertwined regulators: hypoxia pathway proteins, microRNAs, and phosphodiesterases in the control of steroidogenesis
- PMID: 38355819
- PMCID: PMC11310285
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-024-02921-4
Intertwined regulators: hypoxia pathway proteins, microRNAs, and phosphodiesterases in the control of steroidogenesis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Intertwined regulators: hypoxia pathway proteins, microRNAs, and phosphodiesterases in the control of steroidogenesis.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Jan;477(1):169. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03044-6. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 39601889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
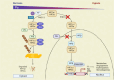
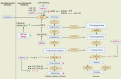
Oxygen sensing is of paramount importance for maintaining cellular and systemic homeostasis. In response to diminished oxygen levels, the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) orchestrate various biological processes. These pivotal transcription factors have been identified as key regulators of several biological events. Notably, extensive research from our group and others has demonstrated that HIF1α exerts an inverse regulatory effect on steroidogenesis, leading to the suppression of crucial steroidogenic enzyme expression and a subsequent decrease in steroid levels. These steroid hormones occupy pivotal roles in governing a myriad of physiological processes. Substantial or prolonged fluctuations in steroid levels carry detrimental consequences across multiple organ systems and underlie various pathological conditions, including metabolic and immune disorders. MicroRNAs serve as potent mediators of multifaceted gene regulatory mechanisms, acting as influential epigenetic regulators that modulate a broad spectrum of gene expressions. Concomitantly, phosphodiesterases (PDEs) play a crucial role in governing signal transduction. PDEs meticulously manage intracellular levels of both cAMP and cGMP, along with their respective signaling pathways and downstream targets. Intriguingly, an intricate interplay seems to exist between hypoxia signaling, microRNAs, and PDEs in the regulation of steroidogenesis. This review highlights recent advances in our understanding of the role of microRNAs during hypoxia-driven processes, including steroidogenesis, as well as the possibilities that exist in the application of HIF prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitors for the modulation of steroidogenesis.
Keywords: Hypoxia; MicroRNA; Phosphodiesterases; Regulation; Steroidogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF1α controls steroidogenesis under acute hypoxic stress.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 13;23(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02080-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39948619 Free PMC article.
-
HIF1α is a direct regulator of steroidogenesis in the adrenal gland.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Apr;78(7):3577-3590. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03750-1. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33464382 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: a novel therapeutic target.Angiogenesis. 2018 May;21(2):183-202. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9600-2. Epub 2018 Jan 27. Angiogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29383635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterases and adrenal Cushing in mice and humans.Horm Metab Res. 2014 Nov;46(12):863-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1389916. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Horm Metab Res. 2014. PMID: 25232906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for microRNA-mediated regulation of steroidogenesis by hypoxia.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Jan 20;49(2):1138-47. doi: 10.1021/es504676s. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25496461
Cited by
-
From Vessels to Neurons-The Role of Hypoxia Pathway Proteins in Embryonic Neurogenesis.Cells. 2024 Apr 3;13(7):621. doi: 10.3390/cells13070621. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF1α controls steroidogenesis under acute hypoxic stress.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 13;23(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02080-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39948619 Free PMC article.
-
How do cells sense oxygen?Pflugers Arch. 2024 Sep;476(9):1303-1305. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03000-4. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 39101995 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akhtar S, Hartmann P, Karshovska E, Rinderknecht FA, Subramanian P, Gremse F, Grommes J, Jacobs M, Kiessling F, Weber C, Steffens S, Schober A (2015) Endothelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha promotes atherosclerosis and monocyte recruitment by upregulating microRNA-19a. Hypertension 66:1220–1226. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05886 - PubMed
-
- Alfar EA, El-Armouche A, Guan K (2018) MicroRNAs in cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation. Cardiovasc Res 114:779–781. 10.1093/cvr/cvy065 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CRC/Transregio 205/1, Project No. 314061271 - TRR205, "The Adrenal: Central Relay in Health and Disease" (A02) to B.W. and A.E.-A.; DFG grants WI3291/12-1 and 13-1 to B.W, EL 270/7-3 to A.E.-A., KA 4194/3-3 to S.K../Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- This work was also supported by a grant from the DFG priority program µBONE 2084 to B.W.; project no. 288034826 - international research training group (IRTG) 2251 to A.E.A. and S.K./Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

