Distinct characteristics of the DNA damage response in mammalian oocytes
- PMID: 38355825
- PMCID: PMC10907590
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01178-2
Distinct characteristics of the DNA damage response in mammalian oocytes
Abstract
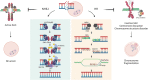
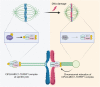
DNA damage is a critical threat that poses significant challenges to all cells. To address this issue, cells have evolved a sophisticated molecular and cellular process known as the DNA damage response (DDR). Among the various cell types, mammalian oocytes, which remain dormant in the ovary for extended periods, are particularly susceptible to DNA damage. The occurrence of DNA damage in oocytes can result in genetic abnormalities, potentially leading to infertility, birth defects, and even abortion. Therefore, understanding how oocytes detect and repair DNA damage is of paramount importance in maintaining oocyte quality and preserving fertility. Although the fundamental concept of the DDR is conserved across various cell types, an emerging body of evidence reveals striking distinctions in the DDR between mammalian oocytes and somatic cells. In this review, we highlight the distinctive characteristics of the DDR in oocytes and discuss the clinical implications of DNA damage in oocytes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

