Water intake, baseline biopsy, and graft function after living donor kidney transplantation
- PMID: 38355944
- PMCID: PMC10866883
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54163-0
Water intake, baseline biopsy, and graft function after living donor kidney transplantation
Abstract
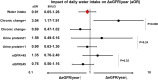
Increased water intake is recommended for kidney transplant recipients; however, its efficacy remains controversial. We hypothesized that pre-existing histological findings of the allograft might modulate the impact of water intake. We retrospectively analyzed 167 adults with living-donor kidney transplants (April 2011-May 2020; median observation period, 77 months) whose baseline biopsy data were available. We compared the chronic-change group (n = 38) with the control group (n = 129) to assess the impact of self-reported daily water intake on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The range distribution of water intake was as follows: - 1000 ml (n = 4), 1000-1500 ml (n = 23), 1500-2000 ml (n = 64), 2000-2500 ml (n = 57), 2500-3000 ml (n = 16), and 3000 - ml (n = 3). Donor age was significantly higher in the chronic-change group. In the control group, the ΔeGFR/year increase was correlated with water intake. However, the increase in the water intake of the chronic-change group significantly decreased ΔeGFR/year (1000-1500 ml: + 1.95 ml/min/1.73 m2 and > 2000 ml: - 1.92 ml/min/1.73 m2, p = 0.014). This study suggested a potential influence of increased water intake on recipients with marginal grafts in living donor kidney transplantation.
Keywords: Biopsy; Graft function; Kidney transplantation; Water intake.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between a change in donor kidney function and long-term allograft outcomes in kidney transplant recipients.Artif Organs. 2015 Mar;39(3):254-9. doi: 10.1111/aor.12367. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Artif Organs. 2015. PMID: 25205383
-
Impact of the pre-transplant histological score on 3-year graft outcomes of kidneys from marginal donors: a single-centre study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Oct;28(10):2637-44. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft292. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23904398 Clinical Trial.
-
Parental donors in live-donor kidney transplantation associated with increased rejection rates and reduced glomerular filtration rates.Transplantation. 2007 Oct 27;84(8):972-80. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000284987.35214.66. Transplantation. 2007. PMID: 17989602
-
Pre-existing arteriosclerotic intimal thickening in living-donor kidneys reflects allograft function.Am J Nephrol. 2012;36(2):127-35. doi: 10.1159/000340035. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Am J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22797609
-
Kidney Transplantation From Old Deceased Donors: Impact of Uric Acid Level-A Quarter-Century of Experience in One Transplant Center.Transplant Proc. 2018 Jul-Aug;50(6):1701-1704. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.02.127. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Transplant Proc. 2018. PMID: 30056885
References
-
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, N., and Allergies Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for water. EFSA J. 2010;8:1459. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1459. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

