Catalyst-free late-stage functionalization to assemble α-acyloxyenamide electrophiles for selectively profiling conserved lysine residues
- PMID: 38355988
- PMCID: PMC10866925
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01107-4
Catalyst-free late-stage functionalization to assemble α-acyloxyenamide electrophiles for selectively profiling conserved lysine residues
Abstract
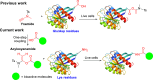
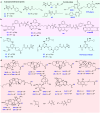
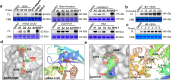
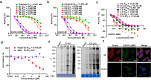
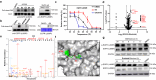
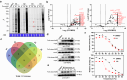
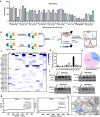
Covalent probes coupled with chemical proteomics represent a powerful method for investigating small molecule and protein interactions. However, the creation of a reactive warhead within various ligands to form covalent probes has been a major obstacle. Herein, we report a convenient and robust process to assemble a unique electrophile, an α-acyloxyenamide, through a one-step late-stage coupling reaction. This procedure demonstrates remarkable tolerance towards other functional groups and facilitates ligand-directed labeling in proteins of interest. The reactive group has been successfully incorporated into a clinical drug targeting the EGFR L858R mutant, erlotinib, and a pan-kinase inhibitor. The resulting probes have been shown to be able to covalently engage a lysine residue proximal to the ATP-binding pocket of the EGFR L858R mutant. A series of active sites, and Mg2+, ATP-binding sites of kinases, such as K33 of CDK1, CDK2, CDK5 were detected. This is the first report of engaging these conserved catalytic lysine residues in kinases with covalent inhibition. Further application of this methodology to natural products has demonstrated its success in profiling ligandable conserved lysine residues in whole proteome. These findings offer insights for the development of new targeted covalent inhibitors (TCIs).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ynamide Electrophile for the Profiling of Ligandable Carboxyl Residues in Live Cells and the Development of New Covalent Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2022 Aug 11;65(15):10408-10418. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00272. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35880853
-
Global Profiling Lysine Reactivity and Ligandability with Oxidant-Triggered Bioconjugation Chemistry.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Feb 3;64(6):e202418473. doi: 10.1002/anie.202418473. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39543955
-
Cell-active, irreversible covalent inhibitors that selectively target the catalytic lysine of EGFR by using fluorosulfate-based SuFEx chemistry.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Nov 5;259:115671. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115671. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37499291
-
N-Acyl-N-alkyl/aryl Sulfonamide Chemistry Assisted by Proximity for Modification and Covalent Inhibition of Endogenous Proteins in Living Systems.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jan 7;58(1):87-100. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00628. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 39661110 Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:395-411. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30500458 Review.
Cited by
-
Ynamide Coupling Reagents: Origin and Advances.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Mar 19;57(6):855-869. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00743. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38452397 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivity-Tunable Fluorescent Platform for Selective and Biocompatible Modification of Cysteine or Lysine.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(31):e2402838. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402838. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38896788 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

