Identifying genetic susceptibility to Aspergillus fumigatus infection using collaborative cross mice and RNA-Seq approach
- PMID: 38356021
- PMCID: PMC10961901
- DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12386
Identifying genetic susceptibility to Aspergillus fumigatus infection using collaborative cross mice and RNA-Seq approach
Abstract
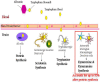
Background: Aspergillus fumigatus (Af) is one of the most ubiquitous fungi and its infection potency is suggested to be strongly controlled by the host genetic background. The aim of this study was to search for candidate genes associated with host susceptibility to Aspergillus fumigatus (Af) using an RNAseq approach in CC lines and hepatic gene expression.
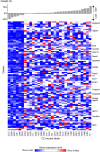
Methods: We studied 31 male mice from 25 CC lines at 8 weeks old; the mice were infected with Af. Liver tissues were extracted from these mice 5 days post-infection, and next-generation RNA-sequencing (RNAseq) was performed. The GENE-E analysis platform was used to generate a clustered heat map matrix.
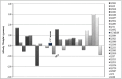
Results: Significant variation in body weight changes between CC lines was observed. Hepatic gene expression revealed 12 top prioritized candidate genes differentially expressed in resistant versus susceptible mice based on body weight changes. Interestingly, three candidate genes are located within genomic intervals of the previously mapped quantitative trait loci (QTL), including Gm16270 and Stox1 on chromosome 10 and Gm11033 on chromosome 8.
Conclusions: Our findings emphasize the CC mouse model's power in fine mapping the genetic components underlying susceptibility towards Af. As a next step, eQTL analysis will be performed for our RNA-Seq data. Suggested candidate genes from our study will be further assessed with a human cohort with aspergillosis.
Keywords: RNA‐Seq; aspergillus fumigatus infection; collaborative cross (CC) mice; gene expression profile; gene‐network; host susceptibility; quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping.
© 2024 The Authors. Animal Models and Experimental Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Chinese Association for Laboratory Animal Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this study and that no competing financial interests exist. Fuad A. Iraqi is an Editorial Board member of AMEM and a co‐author of this article. To minimize bias, he was excluded from all editorial decision‐making related to the acceptance of this article for publication.
Figures

References
-
- The Aspergillus. http://www.aspergillus.org.uk
-
- CDC: Centre for disease control and prevention site. http://www.cdc.gov
-
- Wiecker TS, Luther H, Buettner P, Bauer J, Garbe C. Moderate sun exposure and nevus counts in parents are associated with development of melanocytic nevi in childhood: a risk factor study in 1812 kindergarten children. Cancer. 2003;97(3):628‐638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

