Distinct Assembly Processes Structure Planktonic Bacterial Communities Among Near- and Offshore Ecosystems in the Yangtze River Estuary
- PMID: 38356037
- PMCID: PMC11385042
- DOI: 10.1007/s00248-024-02350-x
Distinct Assembly Processes Structure Planktonic Bacterial Communities Among Near- and Offshore Ecosystems in the Yangtze River Estuary
Abstract
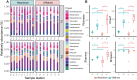
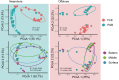
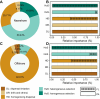
The estuarine system functions as natural filters due to its ability to facilitate material transformation, planktonic bacteria play a crucial role in the cycling of complex nutrients and pollutants within estuaries, and understanding the community composition and assembly therein is crucial for comprehending bacterial ecology within estuaries. Despite extensive investigations into the composition and community assembly of two bacterial fractions (free-living, FLB; particle-attached, PAB), the process by which bacterioplankton communities in these two habitats assemble in the nearshore and offshore zones of estuarine ecosystems remains poorly understood. In this study, we conducted sampling in the Yangtze River Estuary (YRE) to investigate potential variations in the composition and community assembly of FLB and PAB in nearshore and offshore regions. We collected 90 samples of surface, middle, and bottom water from 16 sampling stations and performed 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis along with environmental factor measurements. The results unveiled that the nearshore communities demonstrated significantly greater species richness and Chao1 indices compared to the offshore communities. In contrast, the nearshore communities had lower values of Shannon and Simpson indices. When compared to the FLB, the PAB exhibit a higher level of biodiversity and abundance. However, no distinct alpha and beta diversity differences were observed between the bottom, middle, and surface water layers. The community assembly analysis indicated that nearshore communities are predominantly shaped by deterministic processes, particularly due to heterogeneous selection of PAB; In contrast, offshore communities are governed more by stochastic processes, largely due to homogenizing dispersal of FLB. Consequently, the findings of this study demonstrate that nearshore and PAB communities exhibit higher levels of species diversity, while stochastic and deterministic processes exert distinct influences on communities among near- and offshore regions. This study further sheds new light on our understanding of the mechanisms governing bacterial communities in estuarine ecosystems.
Keywords: Community assembly; Free-living; Nearshore; Offshore; Particle-attached; Yangtze River Estuary.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Santos M, Amorim A, Brotas V, Cruz JPC, Palma C, Borges C, Favareto LR, Veloso V, Damaso-Rodrigues ML, Chainho P, Felix PM, Brito AC (2022) Spatio-temporal dynamics of phytoplankton community in a well-mixed temperate estuary (Sado Estuary, Portugal). Sci Rep 12:16423. 10.1038/s41598-022-20792-6 10.1038/s41598-022-20792-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thibault A, Derenne S, Parlanti E, Anquetil C, Sourzac M, Budzinski H, Fuster L, Laverman A, Roose-Amsaleg C, Viollier E (2019) Dynamics of organic matter in the Seine Estuary (France): bulk and structural approaches. Mar Chem 212:108–119 10.1016/j.marchem.2019.04.007 - DOI
-
- He C, Pan Q, Li P, Xie W, He D, Zhang C, Shi Q (2019) Molecular composition and spatial distribution of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Chem 17:240–251 10.1071/EN19051 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

