Efficacy and Tolerability of Adjunctive Brivaracetam in Patients with Focal-Onset Seizures on Specific Concomitant Antiseizure Medications: Pooled Analysis of Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials
- PMID: 38356105
- PMCID: PMC10960767
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-024-02795-z
Efficacy and Tolerability of Adjunctive Brivaracetam in Patients with Focal-Onset Seizures on Specific Concomitant Antiseizure Medications: Pooled Analysis of Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials
Abstract
Introduction: This article aimed to assess the efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam (BRV) in adults with focal-onset seizures on specific concomitant antiseizure medications (ASMs) taken as part of their treatment regimen.
Methods: This was a post hoc analysis of pooled data from double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (N01252/NCT00490035, N01253/NCT00464269, and N01358/NCT01261325) in patients with uncontrolled focal-onset seizures randomized to BRV (50-200 mg/day) or placebo on the most common concomitant ASMs at trial initiation.
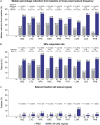
Results: Nine concomitant ASMs were analyzed: carbamazepine (CBZ), lamotrigine (LTG), valproate (VPA), oxcarbazepine (OXC), topiramate (TPM), phenytoin (PHT), lacosamide (LCM), clobazam (CLB), and phenobarbital (PHB). Reduction over placebo in focal-onset seizure frequency per 28 days with BRV ranged from 11.7% (concomitant OXC) to 33.5% (concomitant PHB). The median percentage reduction from baseline in focal-onset seizure frequency per 28 days ranged from 25.5% to 42.8% in patients on BRV (placebo 4.4-21.2%); 50% responder rates ranged from 31.9% to 44.9% in patients on BRV (placebo 11.4-25.2%). In patients on BRV, seizure freedom ranged from 1.4% (concomitant PHT) to 12.5% (concomitant LCM); seizure freedom ranged from 0% to 1.2% in patients on placebo. All efficacy endpoints analyzed were consistently numerically higher in patients on BRV versus placebo. The overall incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) was generally similar across subgroups by specific concomitant ASMs in patients on BRV (range 60.8-74.5%) or placebo (range 53.8-66.7%). Drug-related TEAEs were numerically higher across all subgroups by concomitant ASM in patients on BRV (range 35.2-48.3%) versus placebo (range 23.9-37.1%). Discontinuations due to TEAEs ranged from 2.9% to 13.3% in patients on BRV and was 0-5.7% for patients taking placebo across subgroups.
Conclusion: BRV was efficacious and well tolerated regardless of the specific concomitant ASMs used as part of their treatment regimen. These data show that in patients with focal-onset seizures, BRV provides additional efficacy to a broad range of ASMs.
Keywords: Antiseizure medication; Brivaracetam; Efficacy; Epilepsy; Focal-onset seizures; Tolerability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Brian Moseley, Dimitrios Bourikas, Svetlana Dimova, Sami Elmoufti, and Simon Borghs are salaried employees of UCB Pharma and receive stock or stock options from their employment. Prior to becoming a salaried employee at UCB Pharma, Brian Moseley had previously received honoraria for serving on speaker’s bureaus and advisory boards for UCB Pharma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tolerability and efficacy of adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with focal seizures by concomitant antiseizure medication use: Pooled results from three phase 3 trials.Epilepsia. 2022 Aug;63(8):2024-2036. doi: 10.1111/epi.17304. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Epilepsia. 2022. PMID: 35582748 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of brivaracetam with concomitant lamotrigine or concomitant topiramate in pooled Phase III randomized, double-blind trials: A post-hoc analysis.Epilepsy Behav. 2018 Mar;80:129-134. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.12.024. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Epilepsy Behav. 2018. PMID: 29414542 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Number of Previous Antiseizure Medications on Efficacy and Tolerability of Adjunctive Brivaracetam for Uncontrolled Focal Seizures: Post Hoc Analysis.Adv Ther. 2021 Jul;38(7):4082-4099. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01816-5. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34155568 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in epilepsy: In-depth pooled analysis.Epilepsy Behav. 2020 Feb;103(Pt A):106864. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106864. Epub 2020 Jan 12. Epilepsy Behav. 2020. PMID: 31937513 Review.
-
Narrative Review of Brivaracetam: Preclinical Profile and Clinical Benefits in the Treatment of Patients with Epilepsy.Adv Ther. 2024 Jul;41(7):2682-2699. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02876-z. Epub 2024 May 29. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38811492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Health-Related Quality of Life and Cognitive Performance During 12-Month Adjunctive Brivaracetam Treatment in Patients with Focal-Onset Seizures: A Prospective, Observational Study in Europe.Neurol Ther. 2025 Apr;14(2):609-625. doi: 10.1007/s40120-024-00698-3. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Neurol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39976892 Free PMC article.
-
Brivaracetam: Pharmacology, Clinical Efficacy, and Safety in Epilepsy.J Epilepsy Res. 2025 Jun 10;15(1):42-55. doi: 10.14581/jer.25005. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Epilepsy Res. 2025. PMID: 40568060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- UCB Inc, Smyrna, GA, USA. Briviact® US Prescribing information. 2023. https://www.ucb.com/sites/default/files/2023-05/BRIVIACT_COL_5_2023.pdf. Accessed July 5, 2023.
-
- UCB Pharma, Brussels, Belgium. Briviact® EU Summary of Product Characteristics. 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/briviact-epar.... Accessed July 5, 2023.
-
- Klein P, Schiemann J, Sperling MR, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjunctive brivaracetam in adult patients with uncontrolled partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia. 2015;56(12):1890–1898. doi: 10.1111/epi.13212. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

