Manipulation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Maintenance, Differentiation, and Endocrine Activity of Insulin-Producing Cells: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38356490
- PMCID: PMC10862108
- DOI: 10.30476/ijms.2023.95425.2678
Manipulation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Maintenance, Differentiation, and Endocrine Activity of Insulin-Producing Cells: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Some studies have evaluated the manipulation of the sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway to generate more efficient insulin-producing cells (IPCs). In a systematic review, we evaluated in vitro and in vivo studies on the effect of inhibition or activation of the Shh pathway on the production, differentiation, maintenance, and endocrine activity of IPCs.
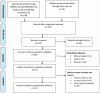
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using all available experimental studies published between January 2000 and November 2022. The review aimed at determining the effect of Shh manipulation on the differentiation of stem cells (SCs) into IPCs. Keywords and phrases using medical subject headings were extracted, and a complete search was performed in Web of Science, Embase, ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane Library databases. The inclusion criteria were manipulation of Shh in SCs, SCs differentiation into IPCs, and endocrine activity of mature IPCs. Articles with incomplete data and duplications were excluded.
Results: A total of 208 articles were initially identified, out of which 11 articles were included in the study. The effect of Shh inhibition in the definitive endoderm stage to produce functional IPCs were confirmed. Some studies showed the importance of Shh re-activation at late-stage differentiation for the generation of efficient IPCs. It is proposed that baseline concentrations of Shh in mature pancreatic β-cells affect insulin secretion and endocrine activities of the cells. However, Shh overexpression in pancreatic β-cells ultimately leads to improper endocrine function and inadequate glucose-sensing insulin secretion.
Conclusion: Accurate manipulation of the Shh signaling pathway can be an effective approach in the production and maintenance of functional IPCs.
Keywords: Hedgehog; Hedgehog proteins; Insulin; Pancreas; Stem cells.
Copyright: © Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Collaboration NCDRF. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387:1513–30. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lin X, Xu Y, Pan X, Xu J, Ding Y, Sun X, et al. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: an analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71908-9. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lucidi P, Porcellati F, Marinelli Andreoli A, Carriero I, Candeloro P, Cioli P, et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of NPH Insulin in Type 1 Diabetes: The Importance of Appropriate Resuspension Before Subcutaneous Injection. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:2204–10. doi: 10.2337/dc15-0801. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources