Kolaviron neuroprotective effect against okadaic acid-provoked cognitive impairment
- PMID: 38356522
- PMCID: PMC10864987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25564
Kolaviron neuroprotective effect against okadaic acid-provoked cognitive impairment
Abstract
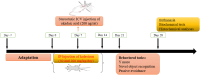
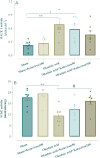
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is acknowledged as the main causative factor of dementia that affects millions of people around the world and is increasing at increasing pace. Okadaic acid (OA) is a toxic compound with ability to inhibit protein phosphatases and to induce tau protein hyperphosphorylation and Alzheimer's-like phenotype. Kolaviron (KV) is a bioflavonoid derived from Garcinia kola seeds with anti-antioxidative and anti-inflammation properties. The main goal of this study was to assess whether kolaviron can exert neuroprotective effect against okadaic acid-induced cognitive deficit. Rats had an intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of OA and pretreated with KV at 50 or 100 mg/kg and examined for cognition besides histological and biochemical factors. OA group treated with KV at 100 mg/kg had less memory deficit in passive avoidance and novel object discrimination (NOD) tasks besides lower hippocampal levels of caspases 1 and 3, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) as inflammatory factors, reactive oxygen species (ROS), protein carbonyl, malondialdehyde (MDA), and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) and higher level of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, mitochondrial integrity index, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione (GSH). Moreover, KV pretreatment at 100 mg/kg attenuated hippocampal CA1 neuronal loss and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) reactivity as a factor of astrogliosis. In summary, KV was able to attenuate cognitive fall subsequent to ICV OA which is partly mediated through its neuroprotective potential linked to mitigation of tau hyperphosphorylation, apoptosis, pyroptosis, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress and also improvement of mitochondrial health.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Apoptosis; Cognition; Inflammation; Kolaviron; Oxidative stress; Pyroptosis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Takeda S. Progression of Alzheimer's disease, tau propagation, and its modifiable risk factors. Neurosci. Res. 2019;141:36–42. - PubMed
-
- Ali G-C G.M., Wu Y.-T., Prince M., Prina M. The Global Impact of Dementia. An analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International. 2015:10–29. 2015.
-
- Atri A. Current and future treatments in Alzheimer's disease. Semin. Neurol. 2019;39(2):227–240. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

