Disruption of Autophagic Flux and Treatment with the PDPK1 Inhibitor GSK2334470 Synergistically Inhibit Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis
- PMID: 38356720
- PMCID: PMC10861819
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.92521
Disruption of Autophagic Flux and Treatment with the PDPK1 Inhibitor GSK2334470 Synergistically Inhibit Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis
Abstract
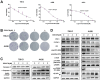
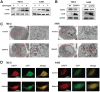
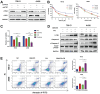
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) frequently exhibits activating PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway mutations. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDPK1 or PDK1) has been established to play a pivotal role in modulating PI3K pathway signaling. mTOR is the main autophagy-initiating factor. However, limited advances have been made in understanding the relationship between PDPK1 and autophagy in RCC. Methods: GSK2334470 (GSK470), a novel and highly specific inhibitor of PDPK1, was selected to investigate the anticancer effects in two RCC cell lines. Cell growth was assessed by CCK-8 test and colony formation. Changes in the protein levels of key Akt/mTOR pathway components and apoptosis markers were assessed by Western blotting. Autophagy was assessed by using LC3B expression, transmission electron microscopy, and a tandem mRFP-EGFP-LC3 construct. The effect of PDPK1 and autophagy inhibitor chloroquine in RCC in vivo was examined in a mouse tumor-bearing model. Results: GSK470 significantly inhibited cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in A498 and 786-O RCC cells. GSK470 downregulates the phosphorylation of PDPK1, thereby inhibiting downstream phosphorylation of Akt1 at Thr308 and Ser473 and mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) activity. Treatment with insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) partially restored GSK470-induced behaviors/activities. Interestingly, treatment of A498 and 786-O cells with GSK470 or siPDPK1 induced significant increases in the hallmarks of autophagy, including autophagosome accumulation, autophagic flux, and LC3B expression. Importantly, GSK470 and chloroquine synergistically inhibited the growth of RCC cells in vitro and in xenograft models, supporting the protective role of autophagy activation upon blockade of the PDPK1-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Conclusion: Our study provides new insight into PDPK1 inhibition combined with autophagy inhibition as a useful treatment strategy for RCC.
Keywords: 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; Autophagy; PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway; Renal cell carcinoma; Targeted therapy.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PDPK1 regulates autophagosome biogenesis by binding to PIK3C3.Autophagy. 2021 Sep;17(9):2166-2183. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1817279. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 32876514 Free PMC article.
-
DRAM1 regulates autophagy and cell proliferation via inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-mTOR-ribosomal protein S6 pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Mar 22;17(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0341-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30902093 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of Avibirnavirus VP3 to the PIK3C3-PDPK1 complex inhibits autophagy by activating the AKT-MTOR pathway.Autophagy. 2020 Sep;16(9):1697-1710. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1704118. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31885313 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Autophagy for Renal Cell Carcinoma Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 7;12(5):1185. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051185. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32392870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Autophagy in Renal Cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Jun 2;10(11):2501-2509. doi: 10.7150/jca.29285. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31258756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Lipworth L, Morgans AK, Edwards TL, Barocas DA, Chang SS, Herrell SD. et al. Renal cell cancer histological subtype distribution differs by race and sex. BJU Int. 2016;117:260–5. - PubMed
-
- Jonasch E. Updates to the Management of Kidney Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16:639–41. - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani AS. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:125–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

