predictive model of nosocomial infection in patients with upper urinary tract stones after flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser lithotripsy: A retrospective study
- PMID: 38356844
- PMCID: PMC10862432
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.8855
predictive model of nosocomial infection in patients with upper urinary tract stones after flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser lithotripsy: A retrospective study
Abstract
Objectives: To construct a predictive model of nosocomial infection in patients with upper urinary tract (UUT) stones after flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser lithotripsy (FURSLL).
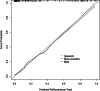
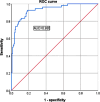
Methods: Medical records of 196 patients with UUT stones who underwent FURSLL in Suzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine from December 2019 to December 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were divided into infected group or uninfected group based on the presence of infection during postoperative hospitalization. Univariate and multivariate logistic regressions were used to identify risk factors of postoperative nosocomial infections. A nomogram prediction model was constructed using R software. The predictive ability of the model was assessed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: A total of 54 patients (27.6%) developed nosocomial infections after FURSLL. Logistic regression analysis showed that older age, diabetes, preoperative urinary system infection, ureteral stricture, hydronephrosis, double J-stent retention time, and stone diameter were risk factors of nosocomial infection. The nomogram model was constructed based on these risk factors. The ROC showed that the area under the curve (AUC) of the model was 0.930 (95% CI: 0.890-0.970), and the sensitivity and specificity were 92.6% and 81.7%, respectively, indicating that the prediction model was effective.
Conclusions: Risk of nosocomial infection in patients with UUT stones after FURSLL is affected by older age, diabetes, preoperative urinary system infection, ureteral stenosis, hydronephrosis, double J-stent retention time, and stone diameter. The nomogram prediction model, constructed based on the above factors, has good predictive value.
Keywords: Flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser lithotripsy; Predictive model; Upper urinary tract stones; nosocomial infection.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The predictive value of ureteral wall area for impacted ureteral stones].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Nov 30;101(44):3637-3642. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210325-00742. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34823280 Chinese.
-
Influencing Factors of Urinary Tract Stones Complicated by Urinary Tract Infections and the Construction of a Column Chart Prediction Model.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2025 May;26(4):209-216. doi: 10.1089/sur.2024.212. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2025. PMID: 39602285
-
Sheathed flexible retrograde intrarenal surgery without safety guide wire for upper urinary tract stones.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2022 Jun 29;94(2):186-189. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2022.2.186. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2022. PMID: 35775345
-
Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome after Flexible Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy.Arch Esp Urol. 2022 Sep;75(7):618-623. doi: 10.56434/j.arch.esp.urol.20227507.89. Arch Esp Urol. 2022. PMID: 36214143
-
Does Retrograde Treatment of Upper Urinary Tract Stones Necessitate Postoperative Upper Urinary Tract Drainage? Conclusions from More Than 500 Single Center Consecutive Cases.J Endourol. 2018 Jun;32(6):477-481. doi: 10.1089/end.2018.0050. Epub 2018 Apr 23. J Endourol. 2018. PMID: 29641353
Cited by
-
Prediction of surgical necessity in children with ureteropelvic junction obstruction using machine learning.Ir J Med Sci. 2025 Apr;194(2):583-590. doi: 10.1007/s11845-025-03895-7. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Ir J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39869146
References
-
- Sorokin I, Mamoulakis C, Miyazawa K, Rodgers A, Talati J, Lotan Y. Epidemiology of stone disease across the world. World J Urol. 2017;35(9):1301–1320. doi:10.1007/s00345-017-2008-6. - PubMed
-
- Chang X, Wang Y, Li J, Han Z. Prestenting versus Nonprestenting on the Outcomes of Flexible Ureteroscopy for Large Upper Urinary Stones:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urol Int. 2021;105(7-8):560–567. doi:10.1159/000506652. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources