Recent advances in zwitterionic nanoscale drug delivery systems to overcome biological barriers
- PMID: 38357524
- PMCID: PMC10861844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100883
Recent advances in zwitterionic nanoscale drug delivery systems to overcome biological barriers
Abstract
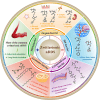
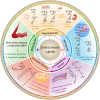
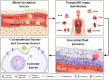
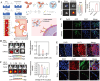
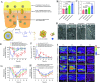
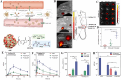
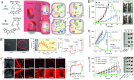
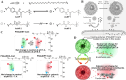
Nanoscale drug delivery systems (nDDS) have been employed widely in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of drugs against diseases with reduced side effects. Although several nDDS have been successfully approved for clinical use up to now, biological barriers between the administration site and the target site hinder the wider clinical adoption of nDDS in disease treatment. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modification (or PEGylation) has been regarded as the gold standard for stabilising nDDS in complex biological environment. However, the accelerated blood clearance (ABC) of PEGylated nDDS after repeated injections becomes great challenges for their clinical applications. Zwitterionic polymer, a novel family of anti-fouling materials, have evolved as an alternative to PEG due to their super-hydrophilicity and biocompatibility. Zwitterionic nDDS could avoid the generation of ABC phenomenon and exhibit longer blood circulation time than the PEGylated analogues. More impressively, zwitterionic nDDS have recently been shown to overcome multiple biological barriers such as nonspecific organ distribution, pressure gradients, impermeable cell membranes and lysosomal degradation without the need of any complex chemical modifications. The realization of overcoming multiple biological barriers by zwitterionic nDDS may simplify the current overly complex design of nDDS, which could facilitate their better clinical translation. Herein, we summarise the recent progress of zwitterionic nDDS at overcoming various biological barriers and analyse their underlying mechanisms. Finally, prospects and challenges are introduced to guide the rational design of zwitterionic nDDS for disease treatment.
Keywords: Biological barrier; Disease treatment; Nano drug delivery system; Targeting delivery; Zwitterionic polymer.
© 2024 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emerging strategies against accelerated blood clearance phenomenon of nanocarrier drug delivery systems.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Feb 25;23(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03209-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40001108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances on next generation of polyzwitterion-based nano-vectors for targeted drug delivery.J Control Release. 2022 Mar;343:492-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Feb 8. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35149143 Review.
-
Responsive Zwitterionic Materials for Enhanced Drug Delivery.Langmuir. 2025 Feb 18;41(6):3744-3756. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c04809. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 39907524 Review.
-
Classification of Nanomaterial Drug Delivery Systems for Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Feb 3;20:1383-1399. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S502546. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39925683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscale drug delivery systems for controllable drug behaviors by multi-stage barrier penetration.J Control Release. 2021 Mar 10;331:282-295. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.045. Epub 2020 Aug 29. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 32866590 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral nanomedicine: Advantages, mechanisms and advanced therapies.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jun 5;52:92-122. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.030. eCollection 2025 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40530413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-Based Therapeutics for Airway Inflammatory Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Feb 10;68(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-09019-w. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39928241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging strategies against accelerated blood clearance phenomenon of nanocarrier drug delivery systems.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Feb 25;23(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03209-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40001108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-triggered Fluorescent-Active Antifouling Microgels Having Disulfide Crosslinked Core for the Application of Site-Specific REDOX-Active Drug Delivery to the Triple Negative Cancer Cells MDA-MB-231.J Fluoresc. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s10895-025-04394-9. Online ahead of print. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 40512373 No abstract available.
-
Engineering principles of zwitterionic hydrogels: Molecular architecture to manufacturing innovations for advanced healthcare materials.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 12;33:102085. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102085. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40704012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kong XY, Cheng R, Wang J, Fang Y, Hwang KC. Nanomedicines inhibiting tumor metastasis and recurrence and their clinical applications. Nano Today. 2021;36
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

