Psychometric Testing of HeLD-14 in a Colombian Geriatric Population
- PMID: 38357580
- PMCID: PMC10866630
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/5570671
Psychometric Testing of HeLD-14 in a Colombian Geriatric Population
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this study was to test the validity and reliability of the Colombian version of the Health Literacy in Dentistry (HeLD-14) in older adults.
Materials and methods: A translation and validation study of HeLD-14 was conducted on 384 non-institutionalized older adults attending the Dental Clinic at Universidad Cooperativa from Pasto, Colombia. A cross-cultural adaptation of a multidimensional HeLD-14 was completed, and the psychometric properties of this scale were evaluated through a cross-validation method using an exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Internal consistency was measured with Cronbach's alpha (α) and Omega's McDonald (ɷ). The statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
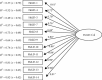
Results: The EFA demonstrated that a single-factor structure with 11 items explained a cumulative 59.86% of the overall variance. The CFA confirmed that goodness of fit indices of this questionnaire had optimal adequateness (χ2S-B = 109.047; χ2S-B/(44) = 2.478, P=0.001; non-normed fit index = 0.901; comparative fit index = 0.908; root mean square error of approximation = 0.079 (90% CI (0.075, 0.083)); standardized root mean residual = 0.080). The coefficients indicated a high internal consistency for the total scale (α = 0.94; ɷ = 0.96).
Conclusion: The developed adaptation of HeLD-14 for the Colombian population, HeLD-Col, is a unidimensional, reliable, and valid instrument to assess oral health literacy in older adults in Colombia.
Copyright © 2024 Ana Cristina Mafla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ratzan S. C., Parker R. M. Introduction. In: Selden C. R., Zorn M., Ratzan S. C., Parker R. M., editors. National Library of Medicine Current Bibliographies in Medicine: Health Literacy . National Institutes of Health; 2020. NLM Publ. No. CBM 2000–1.
-
- American Dental Association (ADA) Health literacy in dentistry. 2022. https://www.ada.org/resources/community-initiatives/health-literacy-in-d... .
-
- Nutbeam D. Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for a contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International . 2000;15(3):259–267. doi: 10.1093/heapro/15.3.259. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources