Optical Coherence Tomography in a Morning Glory Disc Anomaly with a Peripapillary Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
- PMID: 38357615
- PMCID: PMC10863349
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2023.2255665
Optical Coherence Tomography in a Morning Glory Disc Anomaly with a Peripapillary Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
Abstract
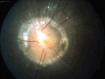
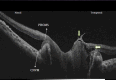
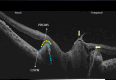
The purpose of this case report is to describe the optical coherence tomography (OCT) features of a peripapillary choroidal neovascular membrane (PPCNVM) in an eye with morning glory disc anomaly (MGDA). A PPCNVM appears as a hyper-reflective mass in the peripapillary area. It should be distinguished from peripapillary hyper-reflective ovoid mass-like structures, which are markers of axoplasmic flow stasis. This case report describes the distinguishing features between the two. The presence of intraretinal cystic spaces are indicative of an active PPCNVM. In conclusion, MGDA can be associated with PPCNVM and OCT can be used in its detection.
Keywords: Optical coherence tomography; congenital optic disc anomaly; morning glory disc anomaly; peripapillary choroidal neovascular membrane; peripapillary hyper-reflective ovoid mass-like structures.
© 2023 Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Fraser JA, Sibony PA, Petzold A, Thaung C, Hamann S, ODDS Consortium . Peripapillary Hyper-reflective Ovoid Mass-like Structure (PHOMS): an optical coherence tomography marker of axoplasmic stasis in the optic nerve head. J Neuroophthalmol. 2021;41(4):431–441. doi:10.1097/WNO.0000000000001203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
