Natural flavonoids as potential therapeutics in the management of Alzheimer's disease: a review
- PMID: 38357675
- PMCID: PMC10861420
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-024-03925-8
Natural flavonoids as potential therapeutics in the management of Alzheimer's disease: a review
Abstract
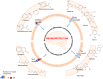
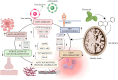
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-dependent neurodegenerative disorder which is associated with the accumulation of proteotoxic Aβ peptides, and pathologically characterized by the deposition of Aβ-enriched plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Given the social and economic burden caused by the rising frequency of AD, there is an urgent need for the development of appropriate therapeutics. Natural compounds are gaining popularity as alternatives to synthetic drugs due to their neuroprotective properties and higher biocompatibility. While natural compound's therapeutic effects for AD have been recently investigated in numerous in vitro and in vivo studies, only few have developed to clinical trials. The present review aims to provide a brief overview of the therapeutic effects, new insights, and upcoming perspectives of the preclinical and clinical trials of flavonoids for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Clinical trials; Flavonoids; Natural products; Neuroprotection.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agullo G, Gamet-Payrastre L, Manenti S, Viala C, Rémésy C, Chap H, Payrastre B. Relationship between flavonoid structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53(11):1649–1657. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(97)82453-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ali T, Kim T, Rehman SU, Khan MS, Amin FU, Khan M, Ikram M, Kim MO. Natural dietary supplementation of anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(7):6076–6093. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0798-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

