Effect of White Noise Intervention Combined with Multi-dimensional Nursing Mode on Sleep Quality and Incidence of Nosocomial Infection in Patients Undergoing Hip Replacement
- PMID: 38358237
- PMCID: PMC10849012
- DOI: 10.4103/nah.nah_32_23
Effect of White Noise Intervention Combined with Multi-dimensional Nursing Mode on Sleep Quality and Incidence of Nosocomial Infection in Patients Undergoing Hip Replacement
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the clinical effects of white noise intervention combined with multi-dimensional nursing mode in patients receiving hip replacement (HR).
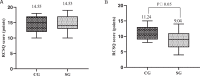
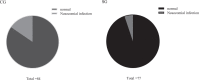
Methods: The study selected the clinical data of 161 patients who underwent HR in our hospital from February 2020 to February 2022 for retrospective analysis. According to patients' willingness, they were divided into the study group (n = 77, receiving white noise intervention combined with multi-dimensional nursing mode) and the control group (n = 84, receiving routine nursing). Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI) scale was used to evaluate patients' sleep quality in the two groups, and the incidence of nosocomial infection in the both groups was counted.
Results: Before nursing and white noise intervention, the PSQI scores of patients' sleep quality in the two groups were all lower, with no obvious difference (P > 0.05). After nursing and white noise intervention, the sleep quality of the two groups was all improved, and the study group had overtly lower PSQI score and score of psychological status than the control group (P < 0.05). After nursing and white noise intervention, the study group had remarkably lower incidence of nosocomial infection than the control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: White noise intervention combined with multi-dimensional nursing mode can effectively improve the sleep quality of patients undergoing HR and reduce the incidence of nosocomial infection, which is of positive significance for promoting the recovery of postoperative limb function.
Keywords: hip replacement; nosocomial infection; sleep quality; white nose intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ye X, Chen JQ, Zhu LL, et al. Intervention strategies for white noise alleviating procedural pain in newborns: a systematic review. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32:4265–82. - PubMed
-
- Riedy Samantha M, Smith Michael G, Rocha S, et al. Noise as a sleep aid: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. 2021;55:101385. - PubMed
-
- Cynthia K, Maldonado David R, Go Cammille C, et al. Mid- to long-term outcomes of hip arthroscopy: a systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2021;37:1011–25. - PubMed
-
- de Brito Artur FS, Brito Nayara C, Tanaka Sandra KT, et al. Thromboprophylaxis of patients submitted to total hip and knee arthroplasty: a cost-effectiveness assessment from the perspective of the Brazilian National Health system. Value Health Reg Issues. 2022;31:111–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

