Evaluation of immature granulocyte parameters in myeloid neoplasms assayed by Sysmex XN hematology analyzer
- PMID: 38358601
- PMCID: PMC10869398
- DOI: 10.1007/s12308-022-00484-w
Evaluation of immature granulocyte parameters in myeloid neoplasms assayed by Sysmex XN hematology analyzer
Abstract
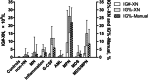
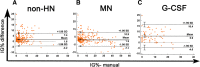
Immature granulocytes (IGs) have significance for the diagnosis of myeloid neoplasms (MNs). The current study aims to use a hematology analyzer to evaluate the accuracy of IG parameters in MNs. Blood specimens from 388 patients with MN, 524 with non-hematological neoplasms (non-HNs), including 109 patients with inflammation and 68 undergoing G-CSF administration, and 500 healthy control subjects were analyzed. IG parameters was assayed by Sysmex XN-9000 (XN) and compared with manual assessments. A high level of agreement between IG% derived from XN and manual measurements for MN patients (r = 0.828, p < 0.0001) was revealed but only a moderate correlation for acute myeloid leukemia patients (AML; r = 0.597; p < 0.0001). Bland-Altman bias analysis was conducted, and the results showed that differences in IG% from XN and manual analysis for MN patients were considered clinically insignificant. ROC analysis demonstrated a good performance of IG# (AUC = 0.842) and IG% (AUC = 0.885) assessed by XN for MN patients with cut-off values of 0.200 × 109/L and 1.95%, respectively. IG parameters from Sysmex XN analyzer are helpful for screening of MNs even though granulocyte morphological abnormalities may interfere with IG parameter accuracy.
Keywords: Hematology analyzer; Immature granulocytes; Morphological abnormalities; Myeloid neoplasms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reporting Sysmex XN Absolute Neutrophil Count in Samples with Leukocyte Analyzer Flagging.Lab Med. 2021 Mar 15;52(2):168-173. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmaa058. Lab Med. 2021. PMID: 32816034
-
Performance evaluation of Sysmex XN hematology analyzer in umbilical cord blood: a comparison study with Sysmex XE-2100.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014 Dec;52(12):1771-9. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2014-0392. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 24978899
-
Validation of the Sysmex XN-V hematology analyzer for canine specimens.Vet Clin Pathol. 2021 Jun;50(2):184-197. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12936. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Vet Clin Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34152026 Free PMC article.
-
Blast flagging of the Sysmex XN-10 hematology analyzer with supervised cell image analysis: Impact on quality parameters.Int J Lab Hematol. 2019 Oct;41(5):601-606. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13069. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Int J Lab Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31162809
-
Performance evaluation of the Sysmex XN-1000V in side-by-side comparison with the Siemens ADVIA 120 and manual methods for healthy CD Sprague-Dawley rats and CD-1 mice.Vet Clin Pathol. 2024 Mar;53(1):8-39. doi: 10.1111/vcp.13314. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Vet Clin Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38164989
Cited by
-
New Neutrophil Parameters in Diseases with Various Inflammatory Processes.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 4;12(9):2016. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092016. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335529 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating myeloid populations have prognostic utility in alcohol-related liver disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 13;15:1330536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1330536. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38545104 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of New Neutrophil-Related Hematologic Parameters in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;15(9):2488. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092488. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173954 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

