ARID1A loss is associated with increased NRF2 signaling in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 38358974
- PMCID: PMC10868765
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297741
ARID1A loss is associated with increased NRF2 signaling in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
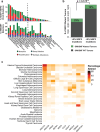
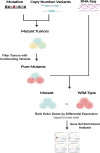
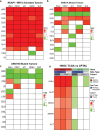
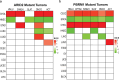
Prior to the next generation sequencing and characterization of the tumor genome landscape, mutations in the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex and the KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway were underappreciated. While these two classes of mutations appeared to independently contribute to tumor development, recent reports have demonstrated a mechanistic link between these two regulatory mechanisms in specific cancer types and cell models. In this work, we expand upon these data by exploring the relationship between mutations in BAF and PBAF subunits of the SWI/SNF complex and activation of NRF2 signal transduction across many cancer types. ARID1A/B mutations were strongly associated with NRF2 transcriptional activity in head and neck squamous carcinomas (HNSC). Many additional tumor types showed significant association between NRF2 signaling and mutation of specific components of the SWI/SNF complex. Different effects of BAF and PBAF mutations on the polarity of NRF2 signaling were observed. Overall, our results support a context-dependent functional link between SWI/SNF and NRF2 mutations across human cancers and implicate ARID1A inactivation in HPV-negative HNSC in promoting tumor progression and survival through activation of the KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway. The tumor-specific effects of these mutations open a new area of study for how mutations in the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway and the SWI/SNF complex contribute to cancer.
Copyright: © 2024 Nguyen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

