Biomimetic nanodrug targets inflammation and suppresses YAP/TAZ to ameliorate atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38359507
- PMCID: PMC11479593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122505
Biomimetic nanodrug targets inflammation and suppresses YAP/TAZ to ameliorate atherosclerosis
Abstract
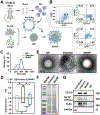
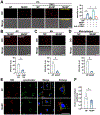
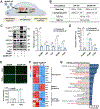
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease, is the primary cause of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. Recent studies have demonstrated that dysregulation of yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding domain (TAZ) contributes to plaque development, making YAP/TAZ potential therapeutic targets. However, systemic modulation of YAP/TAZ expression or activities risks serious off-target effects, limiting clinical applicability. To address the challenge, this study develops monocyte membrane-coated nanoparticles (MoNP) as a targeted delivery system for activated and inflamed endothelium lining the plaque surface. The MoNP system is used to deliver verteporfin (VP), aimed at inhibiting YAP/TAZ specifically within arterial regions prone to atherosclerosis. The results reveal that MoNP significantly enhance payload delivery to inflamed endothelial cells (EC) while avoiding phagocytic cells. When administered in mice, MoNP predominantly accumulate in intima of the atheroprone artery. MoNP-mediated delivery of VP substantially reduces YAP/TAZ expression, thereby suppressing inflammatory gene expression and macrophage infiltration in cultured EC and mouse arteries exposed to atherogenic stimuli. Importantly, this targeted VP nanodrug effectively decreases plaque development in mice without causing noticeable histopathological changes in major organs. Collectively, these findings demonstrate a lesion-targeted and pathway-specific biomimetic nanodrug, potentially leading to safer and more effective treatments for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Inflammation; Nanomedicine; Targeted delivery; YAP/TAZ.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Kuei-Chun Wang reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health and American Heart Association.
Figures
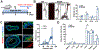

References
-
- Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker SD, Kastelein JJP, Cornel JH, Pais P, Pella D, Genest J, Cifkova R, Lorenzatti A, Forster T, Kobalava Z, Vida-Simiti L, Flather M, Shimokawa H, Ogawa H, Dellborg M, Rossi PRF, Troquay RPT, Libby P, Glynn RJ, CANTOS Trial Group, Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease, N Engl J Med 377 (2017) 1119–1131. 10.1056/NEJMoa1707914. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nidorf SM, Fiolet ATL, Mosterd A, Eikelboom JW, Schut A, Opstal TSJ, The SHK, Xu X-F, Ireland MA, Lenderink T, Latchem D, Hoogslag P, Jerzewski A, Nierop P, Whelan A, Hendriks R, Swart H, Schaap J, Kuijper AFM, van Hessen MWJ, Saklani P, Tan I, Thompson AG, Morton A, Judkins C, Bax WA, Dirksen M, Alings M, Hankey GJ, Budgeon CA, Tijssen JGP, Cornel JH, Thompson PL, LoDoCo2 Trial Investigators, Colchicine in Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease, N Engl J Med 383 (2020) 1838–1847. 10.1056/NEJMoa2021372. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

