Perioperative considerations for patients exposed to hallucinogens
- PMID: 38359966
- PMCID: PMC11324860
- DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2023-104851
Perioperative considerations for patients exposed to hallucinogens
Abstract
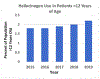
Hallucinogen exposure in patients in the perioperative period presents challenges for anesthesiologists and other anesthesia providers. Acute and chronic exposure to these substances can cause physiological impacts that can affect the function of anesthetic and analgesic medications used during perioperative care. The objective of this narrative review is to educate readers on the wide array of hallucinogens and psychedelics that may influence the perioperative management of patients exposed to these substances. A narrative review of the literature surrounding hallucinogens and psychedelics was completed. Hallucinogens and psychedelics are quite varied in their mechanisms of action and therefore present a variety of perioperative implications and perioperative considerations. Many of these substances increase serotonin levels or act directly at serotonergic receptors. However, there are other relevant actions that may include varied mechanisms from N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonism to stimulation of muscarinic receptors. With hallucinogen exposure rates on the rise, understanding the effects of hallucinogens is important for optimizing management and reducing risks perioperatively for patients with acute or chronic exposure.
Keywords: Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions; Neurotransmitter Agents; Pharmacology.
© American Society of Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine 2024. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: TE: stock/equity: Vanish Therapeutics (nerve stimulator technology start-up).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic Similarities and Differences Among Hallucinogens.J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;61 Suppl 2:S100-S113. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1917. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34396556
-
The Resurgence of Hallucinogen Drugs in Clinical Research.Rev Invest Clin. 2023;75(3):169-178. doi: 10.24875/RIC.23000108. Rev Invest Clin. 2023. PMID: 37441761 Review.
-
Aggressive behaviours associated with MDMA and psychedelics: a narrative review.Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2024 Feb 8;37:e30. doi: 10.1017/neu.2024.3. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2024. PMID: 38329106 Review.
-
Serotonin toxicity of serotonergic psychedelics.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Jun;239(6):1881-1891. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05876-x. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34251464 Review.
-
Hallucinogen persisting perceptual disorder: a scoping review covering frequency, risk factors, prevention, and treatment.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022 Jun;21(6):733-743. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2022.2063273. Epub 2022 May 3. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022. PMID: 35426769
References
-
- Shalit N, Rehm J, and Lev-Ran S, Epidemiology of hallucinogen use in the U.S. results from the National epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions III. Addict Behav, 2019. 89: p. 35–43. - PubMed
-
- Marijuana and hallucinogen use among young adults reached all time-high in 2021. 2022. [cited 2023 01/08]; Available from: https://nida.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/2022/08/marijuana-and-hal....
-
- Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 2021. [cited 2022 May 2]; Available from: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFF....
-
- Nichols DE, Johnson MW, and Nichols CD, Psychedelics as Medicines: An Emerging New Paradigm. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2017. 101(2): p. 209–219. - PubMed
-
- Wang FK-H Why the push to decriminalize psychedelics is growing in Michigan. 2021; Available from: https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/why-the-push-to-decriminalize-psyc....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
