ADARs regulate cuticle collagen expression and promote survival to pathogen infection
- PMID: 38360623
- PMCID: PMC10870475
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-024-01840-1
ADARs regulate cuticle collagen expression and promote survival to pathogen infection
Abstract
Background: In all organisms, the innate immune system defends against pathogens through basal expression of molecules that provide critical barriers to invasion and inducible expression of effectors that combat infection. The adenosine deaminase that act on RNA (ADAR) family of RNA-binding proteins has been reported to influence innate immunity in metazoans. However, studies on the susceptibility of ADAR mutant animals to infection are largely lacking.
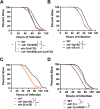
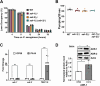
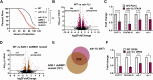
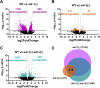
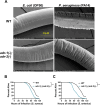
Results: Here, by analyzing adr-1 and adr-2 null mutants in well-established slow-killing assays, we find that both Caenorhabditis elegans ADARs are important for organismal survival to gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, all of which are pathogenic to humans. Furthermore, our high-throughput sequencing and genetic analysis reveal that ADR-1 and ADR-2 function in the same pathway to regulate collagen expression. Consistent with this finding, our scanning electron microscopy studies indicate adr-1;adr-2 mutant animals also have altered cuticle morphology prior to pathogen exposure.
Conclusions: Our data uncover a critical role of the C. elegans ADAR family of RNA-binding proteins in promoting cuticular collagen expression, which represents a new post-transcriptional regulatory node that influences the extracellular matrix. In addition, we provide the first evidence that ADAR mutant animals have altered susceptibility to infection with several opportunistic human pathogens, suggesting a broader role of ADARs in altering physical barriers to infection to influence innate immunity.
Keywords: C. elegans; Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA); Innate immunity; P. aeruginosa; Post-transcriptional regulation; RNA editing; RNA modification; RNA-binding protein.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

