Iron oxide nanoparticles coated with Glucose and conjugated with Safranal (Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal NPs) inducing apoptosis in liver cancer cell line (HepG2)
- PMID: 38360669
- PMCID: PMC10870579
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-024-01142-1
Iron oxide nanoparticles coated with Glucose and conjugated with Safranal (Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal NPs) inducing apoptosis in liver cancer cell line (HepG2)
Abstract
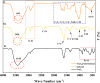
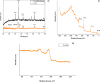
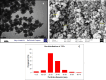
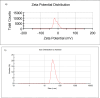
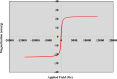
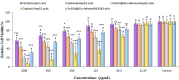
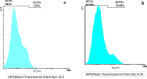
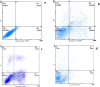
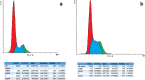
Magnetic nanoparticles can be considered a reliable tool for targeted drug delivery to cancer tissues. Based on this, in this study, the anticancer effect of iron oxide nanoparticles coated with glucose and conjugated with Safranal (Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal NPs) on a liver cancer cell line (HepG2) was investigated. Physicochemical properties of nanoparticles were characterized using FT-IR, XRD, VSM, EDS-mapping, SEM and TEM imaging, zeta potential, and DLS analyses. MTT test was used to investigate the inhibitory effect of nanoparticles on cancer and normal cell lines. Also, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, the population of apoptotic cells, and cell cycle analysis were evaluated in control and nanoparticle-treated cells. The synthesized particles were spherical, in a size range of 17-49 nm, without impurities, with a surface charge of - 13 mV and hydrodynamic size of 129 nm, and with magnetic saturation of 22.5 emu/g. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of Safranal, Fe3O4, Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal and Cisplatin drug on liver cancer cells were 474, 1546, 305 and 135 µg/mL, respectively. While, the IC50 of Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal for normal cell line was 680 µg/mL. Treating liver cancer cells with nanoparticles significantly increased the population of apoptotic cells from 2.5% to 34.7%. Furthermore, the population of the cells arrested at the G2/M phase increased in nanoparticle-treated cells. Due to the biocompatibility of the constituent compounds of these nanoparticles, their magnetic properties, and their inhibitory effects on cancer cells, Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal NPs can be further considered as a promising anticancer compound.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Drug delivery; Fe3O4@Glu-Safranal; Liver cancer; Safranal.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors express no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer mortality and the effect of cinnamon-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles on their expression.Sci Rep. 2025 May 20;15(1):17467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02189-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40394097 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation the cytotoxic effect of Fe3O4@Glu-Gingerol on lung adenocarcinoma cell line (A549) with biological mechanisms.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 10;10(1):e23419. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23419. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38173472 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial potential and cytotoxic activity of iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with thymol (Fe3O4@Glu-Thymol) on breast cancer cells and investigating the expression of BAX, CASP8, and BCL-2 genes.Biometals. 2023 Dec;36(6):1273-1284. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00516-7. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 37351759
-
A novel cobalt oxide nanoparticle conjugated with ellagic acid arrests the cell cycle in human liver cancer cell line.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85312-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805967 Free PMC article.
-
Trigger of apoptosis in human liver cancer cell line (HepG2) by titanium dioxide nanoparticles functionalized by glutamine and conjugated with thiosemicarbazone.3 Biotech. 2023 Jun;13(6):195. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03609-9. Epub 2023 May 16. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37206358 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Wild grown Portulaca oleracea as a novel magnetite based carrier with in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxicity potential.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92495-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082491 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Formulations of Natural Antioxidants for the Treatment of Liver Cancer.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 19;14(8):1031. doi: 10.3390/biom14081031. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Gold, Silver, and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Oncological Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Feb;14(4):e2403059. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202403059. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39501968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver-targeting iron oxide nanoparticles and their complexes with plant extracts for biocompatibility.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024 Dec 11;15:1593-1602. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.15.125. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39691205 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of oncogenes associated with colorectal cancer mortality and the effect of cinnamon-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles on their expression.Sci Rep. 2025 May 20;15(1):17467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02189-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40394097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mushtaq S, Shahzad K, Saeed T, Ul-Hamid A, Abbasi BH, Ahmad N, Khalid W, Atif M, Ali Z, Abbasi R, Abbasi R. Surface functionalized drug loaded spinel ferrite MFe2O4 (M=Fe Co, Ni, Zn) nanoparticles, their biocompatibility and cytotoxicity in vitro: a comparison. Beilstein Arch. 2021;2021(1):56. doi: 10.3762/bxiv.2021.56.v1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
