Lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins are enriched in anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive individuals at risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38360827
- PMCID: PMC10868017
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03274-0
Lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins are enriched in anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive individuals at risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is typically preceded by an extended preclinical period where circulating autoantibodies, particularly anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), are detectable in the absence of clinical arthritis. Increased dietary intake of anti-inflammatory omega-3 (ω3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) has been shown to be associated with a lower the risk of developing incident RA in large epidemiological studies. It is currently not known how changes in fatty acid (FA) metabolism may impact on the progression towards RA in at-risk individuals. To begin to address this question, we profiled serum FAs and oxylipins in an established cohort of at-risk ACPA-positive first-degree relatives (FDR) of RA patients (N = 31), some of whom developed RA (N = 4), and compared their profile to ACPA-negative FDR from the same population (N = 10).
Methods: Gas chromatography (GC) was used for FA quantitation. Oxylipins were extracted and quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS/MS).
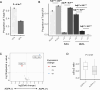
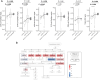
Results: Although we did not detect any meaningful differences in overall FA content between ACPA + and ACPA - FDR, the levels of oxylipins derived from FA metabolism demonstrated significant differences between the two groups, with the ACPA + group demonstrating enrichment in circulating arachidonic acid- and eicosapentaenoic acid-derived molecules. Compared with the ACPA - FDR group, the ACPA + FDR, including those who progressed into inflammatory arthritis, displayed higher levels of LOX-derived oxylipins.
Conclusion: ACPA seropositivity in otherwise unaffected individuals at-risk for developing future RA based on family history (FDR) is associated with alterations in the serum oxylipin profile that suggests dysregulated LOX activity.
Keywords: Fatty acids; Oxylipins; PUFA; Polyunsaturated fatty acids; Preclinical RA; Rheumatoid arthritis; ω-3 fatty acids; ω-6 fatty acids.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional Disability to Evaluate the Risk of Arthritis in First-degree Relatives of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2022 Mar;49(3):244-250. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.210614. Epub 2021 Nov 1. J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34725176
-
Periodontal status correlates with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in first-degree relatives of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Periodontol. 2019 Jul;46(7):690-698. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13117. Epub 2019 May 28. J Clin Periodontol. 2019. PMID: 31025368
-
Association of Antibodies to Citrullinated Protein Antigens with Blood Pressure in First-Degree Relatives of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: The Studies of the Etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Am J Nephrol. 2017;46(6):481-487. doi: 10.1159/000485259. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Am J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 29237149 Free PMC article.
-
Current view on the pathogenic role of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.RMD Open. 2021 Mar;7(1):e001228. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001228. RMD Open. 2021. PMID: 33771834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Rheumatoid Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Jun 26;20(8):50. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0754-0. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29946747 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting dysregulated intracellular immunometabolism within synovial microenvironment in rheumatoid arthritis with natural products.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1403823. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1403823. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39104392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tanner S, Dufault B, Smolik I, Meng X, Anaparti V, Hitchon C, et al. A prospective study of the development of inflammatory arthritis in the family members of Indigenous North American people with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(9):1494–1503. doi: 10.1002/art.40880. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bos WH, Wolbink GJ, Boers M, Tijhuis GJ, de Vries N, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, et al. Arthritis development in patients with arthralgia is strongly associated with anti-citrullinated protein antibody status: a prospective cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(3):490–494. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.105759. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

