Enhanced visualization in endoleak detection through iterative and AI-noise optimized spectral reconstructions
- PMID: 38360941
- PMCID: PMC10869818
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54502-1
Enhanced visualization in endoleak detection through iterative and AI-noise optimized spectral reconstructions
Abstract
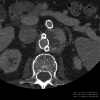
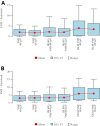
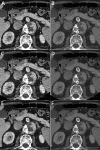
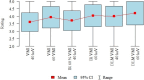
To assess the image quality parameters of dual-energy computed tomography angiography (DECTA) 40-, and 60 keV virtual monoenergetic images (VMIs) combined with deep learning-based image reconstruction model (DLM) and iterative reconstructions (IR). CT scans of 28 post EVAR patients were enrolled. The 60 s delayed phase of DECTA was evaluated. Objective [noise, contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)] and subjective (overall image quality and endoleak conspicuity - 3 blinded readers assessment) image quality analyses were performed. The following reconstructions were evaluated: VMI 40, 60 keV VMI; IR VMI 40, 60 keV; DLM VMI 40, 60 keV. The noise level of the DLM VMI images was approximately 50% lower than that of VMI reconstruction. The highest CNR and SNR values were measured in VMI DLM images. The mean CNR in endoleak in 40 keV was accounted for as 1.83 ± 1.2; 2.07 ± 2.02; 3.6 ± 3.26 in VMI, VMI IR, and VMI DLM, respectively. The DLM algorithm significantly reduced noise and increased lesion conspicuity, resulting in higher objective and subjective image quality compared to other reconstruction techniques. The application of DLM algorithms to low-energy VMIs significantly enhances the diagnostic value of DECTA in evaluating endoleaks. DLM reconstructions surpass traditional VMIs and IR in terms of image quality.
Keywords: Abdominal aortic aneurysms; Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction; Dual-energy computed tomography angiography; Endoleak; Endovascular aneurysm repair; Image reconstruction, deep learning model; Virtual monoenergetic images.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

