Improving the Automated Diagnosis of Breast Cancer with Mesh Reconstruction of Ultrasound Images Incorporating 3D Mesh Features and a Graph Attention Network
- PMID: 38361007
- PMCID: PMC11573965
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-00983-5
Improving the Automated Diagnosis of Breast Cancer with Mesh Reconstruction of Ultrasound Images Incorporating 3D Mesh Features and a Graph Attention Network
Abstract
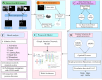
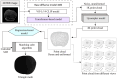
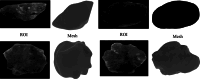
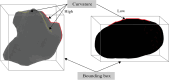
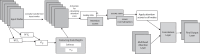
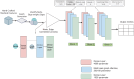
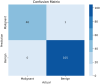
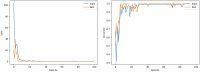
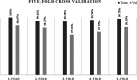
This study proposes a novel approach for breast tumor classification from ultrasound images into benign and malignant by converting the region of interest (ROI) of a 2D ultrasound image into a 3D representation using the point-e system, allowing for in-depth analysis of underlying characteristics. Instead of relying solely on 2D imaging features, this method extracts 3D mesh features that describe tumor patterns more precisely. Ten informative and medically relevant mesh features are extracted and assessed with two feature selection techniques. Additionally, a feature pattern analysis has been conducted to determine the feature's significance. A feature table with dimensions of 445 × 12 is generated and a graph is constructed, considering the rows as nodes and the relationships among the nodes as edges. The Spearman correlation coefficient method is employed to identify edges between the strongly connected nodes (with a correlation score greater than or equal to 0.7), resulting in a graph containing 56,054 edges and 445 nodes. A graph attention network (GAT) is proposed for the classification task and the model is optimized with an ablation study, resulting in the highest accuracy of 99.34%. The performance of the proposed model is compared with ten machine learning (ML) models and one-dimensional convolutional neural network where the test accuracy of these models ranges from 73 to 91%. Our novel 3D mesh-based approach, coupled with the GAT, yields promising performance for breast tumor classification, outperforming traditional models, and has the potential to reduce time and effort of radiologists providing a reliable diagnostic system.
Keywords: Breast tumor; Feature extraction; Graph attention network (GAT); Mesh; Point cloud; Ultrasound.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Graph neural network-based breast cancer diagnosis using ultrasound images with optimized graph construction integrating the medically significant features.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(20):18039-18064. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05464-w. Epub 2023 Nov 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37982829 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Classification in Automated Breast Ultrasound Using Multiview Convolutional Neural Network with Transfer Learning.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 May;46(5):1119-1132. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32059918
-
Medical breast ultrasound image segmentation by machine learning.Ultrasonics. 2019 Jan;91:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Ultrasonics. 2019. PMID: 30029074
-
Automated whole-breast ultrasound tumor diagnosis using attention-inception network.Phys Med. 2025 Jun;134:104989. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2025.104989. Epub 2025 May 14. Phys Med. 2025. PMID: 40373703
-
Three-dimensional automated breast ultrasound: Technical aspects and first results.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019 Oct;100(10):579-592. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30962169 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and Challenges in 3D Bioprinted Cancer Models: Opportunities for Personalized Medicine and Tissue Engineering.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;17(7):948. doi: 10.3390/polym17070948. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40219336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging advanced graph neural networks for the enhanced classification of post anesthesia states to aid surgical procedures.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 25;20(4):e0320299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320299. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40279343 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances and applications of artificial intelligence in 3D bioprinting.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2024 Jul 19;5(3):031301. doi: 10.1063/5.0190208. eCollection 2024 Sep. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2024. PMID: 39036708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Z, Li M, Wang H, Jiang H, Yao Y, Zhang H, et al. Breast Cancer Detection Using Extreme Learning Machine Based on Feature Fusion with CNN Deep Features. IEEE Access 2019;7:105146–58. 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2892795.
-
- Lu SY, Wang SH, Zhang YD. BCDNet: An Optimized Deep Network for Ultrasound Breast Cancer Detection. IRBM 2023;44. 10.1016/j.irbm.2023.100774.
-
- Huang Q, Wang D, Lu Z, Zhou S, Li J, Liu L, et al. A novel image-to-knowledge inference approach for automatically diagnosing tumors. Expert Syst Appl 2023;229. 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120450.
-
- Karthik R, Menaka R, Siddharth MV. Classification of breast cancer from histopathology images using an ensemble of deep multiscale networks. Biocybern Biomed Eng 2022;42:963–76. 10.1016/j.bbe.2022.07.006.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
