Bubble DNA tweezer: A triple-conformation sensor responsive to concentration-ratios
- PMID: 38361618
- PMCID: PMC10867447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109074
Bubble DNA tweezer: A triple-conformation sensor responsive to concentration-ratios
Abstract
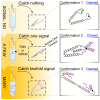
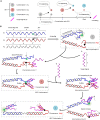
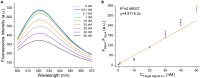
DNA tweezers, with their elegant simplicity and flexibility, have been pivotal in biosensing and DNA computing. However, conventional tweezers are confined to a binary transformation pre/post target signal recognition, limiting them to presence/absence judgments. This study introduces bubble DNA tweezers (BDT), capable of three distinct conformations based on variable target signal ratios. In contrast to traditional compact tweezers, BDT features a looser structure centered around a non-complementary bubble domain located between the tweezer arms' connecting axis and target signal recognition jaws. This bubble triggers toehold-free DNA strand displacement, leading to three conformational changes at different target signal concentrations. BDT detects presence/absence and true concentration with remarkable specificity and sensitivity. This adaptability is not confined to ideal scenarios, proving valuable in complex, noisy environments. Our method facilitates target DNA/miRNA signal quantification within a specific length range, promising applications in clinical research and environmental detection, while inspiring future biological assay innovations.
Keywords: Biophysical chemistry; Biophysics; Chemistry.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Toehold Mediated One-Step Conformation-Switchable "Signal-On" Electrochemical DNA Sensing Enhanced with Homogeneous Enzymatic Amplification.Anal Chem. 2017 May 16;89(10):5349-5356. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b05171. Epub 2017 May 5. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 28452219
-
Dynamical Regulation of Enzyme Cascade Amplification by a Regenerated DNA Nanotweezer for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical DNA Detection.Anal Chem. 2018 Sep 18;90(18):10701-10706. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00477. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 30146880
-
Programmable DNA tweezers-SDA for ultra-sensitive signal amplification fluorescence sensing strategy.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 Mar 1;1292:342245. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342245. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38309853
-
Biocomputing Based on DNA Strand Displacement Reactions.Chemphyschem. 2021 Jun 16;22(12):1151-1166. doi: 10.1002/cphc.202100140. Epub 2021 May 20. Chemphyschem. 2021. PMID: 33871136 Review.
-
Application of DNA Nanotweezers in biosensing: Nanoarchitectonics and advanced challenges.Biosens Bioelectron. 2023 Oct 1;237:115445. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115445. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023. PMID: 37421799 Review.
Cited by
-
Triple-Branch Catalytic Assembly DNAzyme Motivated DNA Tweezer for Sensitive and Reliable mecA Gene Detection in Staphylococcus aureus.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 28;34(12):2450-2456. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2409.09008. Epub 2024 Oct 1. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39467691 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

