Long-term efficacy and safety of nusinersen in adults with 5q spinal muscular atrophy: a prospective European multinational observational study
- PMID: 38361750
- PMCID: PMC10864329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2024.100862
Long-term efficacy and safety of nusinersen in adults with 5q spinal muscular atrophy: a prospective European multinational observational study
Abstract
Background: Evidence for the efficacy of nusinersen in adults with 5q-associated spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) has been demonstrated up to a period of 16 months in relatively large cohorts but whereas patients reach a plateau over time is still to be demonstrated. We investigated the efficacy and safety of nusinersen in adults with SMA over 38 months, the longest time period to date in a large cohort of patients from multiple clinical sites.
Methods: Our prospective, observational study included adult patients with SMA from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria (July 2017 to May 2022). All participants had genetically-confirmed, 5q-associated SMA and were treated with nusinersen according to the label. The total Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale Expanded (HFMSE) and Revised Upper Limb Module (RULM) scores, and 6-min walk test (6 MWT; metres), were recorded at baseline and 14, 26, and 38 months after treatment initiation, and pre and post values were compared. Adverse events were also recorded.
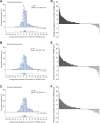
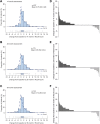
Findings: Overall, 389 patients were screened for eligibility and 237 were included. There were significant increases in all outcome measures compared with baseline, including mean HFMSE scores at 14 months (mean difference 1.72 [95% CI 1.19-2.25]), 26 months (1.20 [95% CI 0.48-1.91]), and 38 months (1.52 [95% CI 0.74-2.30]); mean RULM scores at 14 months (mean difference 0.75 [95% CI 0.43-1.07]), 26 months (mean difference 0.65 [95% CI 0.27-1.03]), and 38 months (mean difference 0.72 [95% CI 0.25-1.18]), and 6 MWT at 14 months (mean difference 30.86 m [95% CI 18.34-43.38]), 26 months (mean difference 29.26 m [95% CI 14.87-43.65]), and 38 months (mean difference 32.20 m [95% CI 10.32-54.09]). No new safety signals were identified.
Interpretation: Our prospective, observational, long-term (38 months) data provides further real-world evidence for the continuous efficacy and safety of nusinersen in a large proportion of adult patients with SMA.
Funding: Financial support for the registry from Biogen, Novartis and Roche.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotide; Intrathecal therapy; Motor neuron disease; Nusinersen; Spinal muscular atrophy.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SB, ZU, MH, TK, KM, BI, JB, MTM, TB, BS, SF, CS, MTo, AG, MTue, MS, CR, PB, MFB, CK, KPS, SG, ST, JN, RS, MWeb, GW and OvV declare no conflicts of interest. RG has received personal fees from Biogen and Hoffmann-La Roche and served on advisory boards from Biogen, Hoffmann-La Roche, ITF Pharma, Zambon and research support from Biogen, outside of the submitted work. CDW has received personal fees from Biogen and Hoffmann–La Roche outside of the submitted work. AO has received speaker fees from Biogen outside of the submitted work. OSK received academic research support from the Hannover Medical School (MHH) and the German Neuromuscular Society “Deutsche Gesellschaft fuer Muskelkranke” (DGM e.V.), 2019–2021 (grant no. Sc 23/1); and received honoraria as a speaker and/or funding for travel expenses from the German Neuromuscular Society “Deutsche Gesellschaft fuer Muskelkranke (DGM e.V.), Biogen GmbH, Biermann Verlag GmbH, and MK + S—Medizin, Kommunikation & Service GmbH, outside the submitted work. SP has received speaker fees, non-financial support and research support from Biogen, Roche, AL-S Pharma, Amylyx, Cytokinetics, Ferrer, ITF-Pharma, Zambon, and Sanofi and served on advisory boards of Amylyx, Biogen, Roche, Zambon and ITF Pharma outside of the submitted work. MCW has served on advisory boards for Avexis, Biogen, Grünenthal, Novartis, Pfizer, PharNext, PTC Therapeutics, Roche, Santhera, Sarepta, Ultragenyx, Wave Sciences, received funding for Travel or Speaker Honoraria from Biogen, Novartis, PTC Therapeutics, Santhera, and worked as an ad-hoc consultant for Affinia, Audentes Therapeutics, Avexis, Biogen, BridgeBio, Edgewise, Fulcrum, Grünenthal, ML Bio, Novartis, Pfizer, PharNEXT, PTC Therapeutics, Roche. MWei has received advisory board and consultant honoraria from Biogen and Hoffmann-La Roche, and speaker honoraria and travel support for conference attendance from Biogen, outside of the submitted work. MW is a member of the European Reference Network for Neuromuscular Diseases (ERN EURO-NMD). MF has received a speaker honorarium and non-financial support from Biogen outside the submitted work. HSL is receiving advisory fees from Biogen but has no financial or non-financial conflict of interest to declare related to the content of this manuscript. IC has received research grants and speaker fees from Biogen and Hoffmann-La Roche, outside of the submitted work. PL has received honoraria for advisory boards and consultancies from Stadapharm, Abbvie, Alexion, Bial, ITF Pharma, Desitin, Novartis, Woolsey Pharma outside the scope of this work. MD has received personal fees as speaker/consultant from Biogen and Roche, outside of the submitted work. Aha received research grants from Novartis Gene Therapies, and advisory board honoraria and speaker fees from Biogen, Roche, and Novartis. AR has received advisory board honoraria from Biogen outside of the submitted work. DZ received compensation from Biogen for participation on advisory boards, from Novartis for consultancy work, and travel compensation from Angelini Pharma outside of the submitted work. JCK has received personal fees from Biogen and Roche for advisory boards and development of educational material outside of this study. AHe has received personal fees and non-financial support from Biogen and Desitin for advisory board meetings outside the reported work. CK has received advisory board honoraria from Biogen, Roche and Ipsen Pharma, speaker honoraria from Biogen and unrestricted travel grants from Ipsen outside of the submitted work. SN has received financial support for consultancy and lecturing from Allergan, Hormosan, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Teva and Medscape, research support from Novartis, all outside of the submitted work. AM has received advisory board honoraria from Hormosan and Sanofi, outside of the submitted work. CN has received personal fees from Biogen and Hoffmann–La Roche outside of the submitted work. HCL received honoraria for speaking and advisory board engagements or academic research support Biogen. MG has received an advisory board honorarium from Hoffmann-La Roche and a speaker fee from Novartis outside of the submitted work. AP received compensation for advisory boards, training activities and research grants from Novartis and Biogen. JK received compensation for clinical research and/or consultancy activities from Biogen, Novartis, Roche and ScholarRock. GB has received research grants from PTC, advisory board honoraria and speaker fees from Biogen, Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, PTC and personal fees from Roche outside of the submitted work. PM has received honorary as an advisory board member from Biogen unrelated to this work. GMzH received compensation for serving on scientific advisory boards (Alexion, Roche, LFB) and speaker honoraria (Alexion). WL received advisory board honoraria and speaker fees from Biogen and Roche outside of the submitted work MFB has received honoraria from Biogen, Roche and Novartis as an advisory board member and for lectures from Novartis. US has received honoraria for counseling at advisory boards and invited talks for Biogen, Novartis and Roche. WMF has received compensation for scientific advisory boards for Biogen, Novartis, PTC, Sarepta, Sanofi-Aventis, Roche and Cytokinetics and received travel expenses and speaker fees from Biogen, Novartis, PTC, Roche, Sarepta and Sanofi-Aventis. HLo received support for research projects and clinical trials from Amplo Biotechnology, AMO Pharma, argenx, Biogen, Desitin, Fulcrum Therapeutics, Harmony Biosciences, KYE Pharmaceuticals, Milo Biotechnology, Novartis, Pfizer, PTC Therapeutics, Hoffman-La Roche Limited, Sanofi-Genzyme, Santhera, Sarepta, Satellos, Spark Therapeutics and Ultragenyx. HL is the Editor-in-chief for the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases (IOS Press). CK has received compensation for lectures and advisory boards as well as research funds from Biogen, Roche and Novartis. ACL is a member of Advisory Boards of Roche Pharma AG, Biogen, Alector and Amylyx. He received compensation for talks from Biologix, the German Society of Neurology, Biogen, Springer Medicine, Amylyx and the company Streamed Up! GmbH. He is involved in trials which are sponsored by Amylyx, Ferrer International, Novartis Research and Development, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Alexion, Orion Pharma, the European Union, BMBF, Biogen and Orphazyme, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, QurAlis and Alector. TH has received research grants, advisory board honoraria and speaker fees from Biogen, Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis and personal fees from Roche and Novartis outside of the submitted work.
Figures




References
-
- Lefebvre S., Burglen L., Reboullet S., et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995;80(1):155–165. - PubMed
-
- Wadman R.I., Wijngaarde C.A., Stam M., et al. Muscle strength and motor function throughout life in a cross-sectional cohort of 180 patients with spinal muscular atrophy types 1c-4. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(3):512–518. - PubMed
-
- Wijngaarde C.A., Stam M., Otto L.A.M., et al. Muscle strength and motor function in adolescents and adults with spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 2020;95(14):e1988–e1998. - PubMed
-
- Dubowitz V. Ramblings in the history of spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2009;19(1):69–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

