Compassion and equity-focused clinical genomics training for health professional learners
- PMID: 38363012
- PMCID: PMC11726403
- DOI: 10.1002/jgc4.1874
Compassion and equity-focused clinical genomics training for health professional learners
Abstract
There remains an urgent need for expanded genomics training in undergraduate medical education, especially as genetic and genomic assessments become increasingly important in primary care and routine clinical practice across specialties. Physician trainees continue to report feeling poorly prepared to provide effective consultation or interpretation of genomic test results. Here we report on the development, pilot implementation, and evaluation of an elective offering for pre-clinical medical students called the Sanford Precision Health Scholars Immersive Learning Experience (PHS), which was designed leveraging genetic counseling expertise as one means to address this need. This 9-week course, piloted in Fall 2021 at UC San Diego, afforded students the opportunity to build technical skills and competencies in clinical genomics while identifying, addressing, and engaging with pervasive health disparities in genomics. Interactive exercises focused students' learning on strategies for empathic and compassionate patient interactions while supporting the application of concepts and knowledge to future practice. Upon completion of the course, participants reported increases in confidence related to skills required for clinical genomics practice. Drawing on learnings from this pilot implementation, recommendations for refining the program include deepening pedagogical engagement with ethical issues, expanding the offering to trainees across health professions, including pharmacy students, and incorporating an optional experiential learning component. Educational offerings, like PHS, that are designed with the input of genetic counseling expertise may ease pressures on the genetic counseling profession by building a more genomic-literate healthcare workforce that can better support efforts to expand access for patients.
Keywords: communication; diversity; education; empathy and compassion; genetic literacy; genetic testing; health equity; precision health.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Genetic Counseling published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of National Society of Genetic Counselors.
Conflict of interest statement
Taylor Berninger, Ramya M. Rajagopalan, and Cinnamon S. Bloss declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

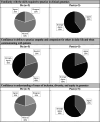
References
-
- Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) . (2021). Medical school graduation questionnaire: 2021 all schools summary report . https://www.aamc.org/media/55736/download
-
- Jonas, M. C. , Suwannarat, P. , Burnett‐Hartman, A. , Carroll, N. , Turner, M. , Janes, K. , Truong, C. , Blum‐Barnett, E. , Aziz, N. , & McGlynn, E. A. (2019). Physician experience with direct‐to‐consumer genetic testing in Kaiser Permanente. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 9(4), 47. 10.3390/jpm9040047 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

