External validation of a red cell-based blood prognostic score in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations
- PMID: 38363410
- PMCID: PMC10973030
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-024-10266-6
External validation of a red cell-based blood prognostic score in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations
Abstract
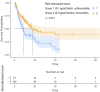
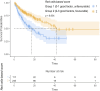
Immunotherapy combinations with tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) had significantly improved outcomes of patients with mRCC. Predictive and prognostic factors are crucial to improve patients' counseling and management. The present study aimed to externally validate the prognostic value of a previously developed red cell-based score, including hemoglobin (Hb), mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and red cell distribution width (RDW), in patients with mRCC treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations (TKI plus ICI or ICI plus ICI). We performed a sub-analysis of a multicentre retrospective observational study (ARON-1 project) involving patients with mRCC treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations. Uni- and multivariable Cox regression models were used to assess the correlation between the red cell-based score and progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Logistic regression were used to estimate the correlation between the score and the objective response rate (ORR). The prognostic impact of the red cell-based score on PFS and OS was confirmed in the whole population regardless of the immunotherapy combination used [median PFS (mPFS): 17.4 vs 8.2 months, HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.47-0.94; median OS (mOS): 42.0 vs 17.3 months, HR 0.60, 95% CI 0.39-0.92; p < 0.001 for both]. We validated the prognostic significance of the red cell-based score in patients with mRCC treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations. The score is easy to use in daily clinical practice and it might improve patient counselling.
Keywords: Blood; Immunotherapy combination; Mean corpuscular volume; Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; Prognostic score; Red cell distribution width.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Rebuzzi received honoraria as speaker at scientific events and travel accomodation by BMS, Amgen, GSK, Janssen, Astellas, Ipsen, MSD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrating Red Blood Cell Features and Hemoglobin Levels in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Treated with Pazopanib or Cabozantinib: An Easily Exploitable Prognostic Score.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2023 Jul 28;15(3):20. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1503020. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2023. PMID: 37743233
-
Role of Hb to RDW ratio in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with first-line immunotherapy combinations.Immunotherapy. 2025 Jan;17(1):25-35. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2452145. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 39829377
-
Efficacy of VEGFR-TKIs plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with favorable IMDC prognosis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Nov;100:102295. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102295. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34564043 Review.
-
Impact of Clinicopathological Features on Survival in Patients Treated with First-line Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Eur Urol Focus. 2022 Mar;8(2):514-521. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Eur Urol Focus. 2022. PMID: 33714725 Review.
-
Real-world Outcome of Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Intermediate- or Poor-risk International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Criteria Treated by Immune-oncology Combinations: Differential Effectiveness by Risk Group?Eur Urol Oncol. 2024 Feb;7(1):102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37481365
Cited by
-
A red blood cell-based score in the prognostication of patients with metastatic RCC of the Meet-URO 15 study.Immunotherapy. 2024;16(14-15):963-973. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2024.2382666. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Immunotherapy. 2024. PMID: 39105621 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Based Biomarkers as Predictive and Prognostic Factors in Immunotherapy-Treated Patients with Solid Tumors-Currents and Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/cancers17122001. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High red blood cell distribution width attenuates the effectiveness of Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: An exploratory study using a clinical data warehouse.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):e0299760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299760. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39088539 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical