Pattern electroretinography response in amblyopic adults
- PMID: 38363441
- PMCID: PMC10873232
- DOI: 10.1007/s10792-024-03042-8
Pattern electroretinography response in amblyopic adults
Abstract
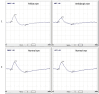
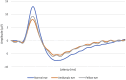
Introduction: Amblyopia is generally a unilateral disorder, defined by at least a difference of two lines of visual acuity between both eyes with the best-corrected visual acuity, a decrease in contrast sensitivity, and a decrease in stereopsis. Pattern electroretinogram (PERG) is a noninvasive technique that provides a retinal biopotential and is a highly sensitive indicator of changes in the macular area. Our aim was to evaluate if there are differences in the retinal response of an amblyopic eye compared with a normal eye (NE).
Methods: We evaluated twenty-four adult volunteers, twelve amblyopes (mean 43.42 ± 12.72 years old), and twelve subjects with NE (mean 35.58 ± 12.85 years old). None of the subjects in the two groups had comorbidities. A complete optometric examination was performed including parameters such as visual acuity (VA) by far and near with ETDRS chart, eye alignment with cover test, and evaluation of retinal cells response with PERG.
Results: The refractive error found in the NE group of subjects had a mean of - 0.95 ± 1.65D, while the amblyopic group showed a mean of - 2.03 ± 4.29D. The VA in amblyopic eyes had a mean of 0.38 ± 0.20 logMAR. Analyzing PERG data, we observed significant differences in the P50-N95 amplitudes of the amblyopic group compared with the NE group (p < 0.0001-amblyopic eye vs. NE; p = 0.039-fellow eye vs. NE).
Discussion: These findings suggest that amblyopic patients may also present other impairments beyond the visual cortex. PERGs seem to be an important complementary examination in the diagnosis of other impairments in amblyopia.
Keywords: Adults; Amblyopia; Electrophysiology; Pattern electroretinography; Retinal disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Holder GE (2001) Pattern electroretinography (PERG) and an integrated approach to visual pathway diagnosis. Prog Retin Eye Res 20(4):531–561 - PubMed
-
- Bach M, Brigell MG, Hawlina M, Holder GE, Johnson MA, McCulloch DL et al (2013) ISCEV standard for clinical pattern electroretinography (PERG): 2012 update. Doc Ophthalmol 126(1):1–7 - PubMed
-
- Clavagnier S, Thompson B, Hess RF (2013) Long lasting effects of daily theta burst rTMS sessions in the human amblyopic cortex. Brain Stimul 6(6):860–867 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

