RNA Interference With Zilebesiran for Mild to Moderate Hypertension: The KARDIA-1 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38363577
- PMCID: PMC10873804
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2024.0728
RNA Interference With Zilebesiran for Mild to Moderate Hypertension: The KARDIA-1 Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Angiotensinogen is the most upstream precursor of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, a key pathway in blood pressure (BP) regulation. Zilebesiran, an investigational RNA interference therapeutic, targets hepatic angiotensinogen synthesis.
Objective: To evaluate antihypertensive efficacy and safety of different zilebesiran dosing regimens.
Design, setting, and participants: This phase 2, randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study of zilebesiran vs placebo was performed at 78 sites across 4 countries. Screening initiation occurred in July 2021 and the last patient visit of the 6-month study occurred in June 2023. Adults with mild to moderate hypertension, defined as daytime mean ambulatory systolic BP (SBP) of 135 to 160 mm Hg following antihypertensive washout, were randomized.
Interventions: Randomization to 1 of 4 subcutaneous zilebesiran regimens (150, 300, or 600 mg once every 6 months or 300 mg once every 3 months) or placebo (once every 3 months) for 6 months.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was between-group difference in least-squares mean (LSM) change from baseline to month 3 in 24-hour mean ambulatory SBP.
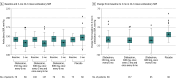
Results: Of 394 randomized patients, 377 (302 receiving zilebesiran and 75 receiving placebo) comprised the full analysis set (93 Black patients [24.7%]; 167 [44.3%] women; mean [SD] age, 57 [11] years). At 3 months, 24-hour mean ambulatory SBP changes from baseline were -7.3 mm Hg (95% CI, -10.3 to -4.4) with zilebesiran, 150 mg, once every 6 months; -10.0 mm Hg (95% CI, -12.0 to -7.9) with zilebesiran, 300 mg, once every 3 months or every 6 months; -8.9 mm Hg (95% CI, -11.9 to -6.0) with zilebesiran, 600 mg, once every 6 months; and 6.8 mm Hg (95% CI, 3.6-9.9) with placebo. LSM differences vs placebo in change from baseline to month 3 were -14.1 mm Hg (95% CI, -19.2 to -9.0; P < .001) with zilebesiran, 150 mg, once every 6 months; -16.7 mm Hg (95% CI, -21.2 to -12.3; P < .001) with zilebesiran, 300 mg, once every 3 months or every 6 months; and -15.7 mm Hg (95% CI, -20.8 to -10.6; P < .001) with zilebesiran, 600 mg, once every 6 months. Over 6 months, 60.9% of patients receiving zilebesiran had adverse events vs 50.7% patients receiving placebo and 3.6% had serious adverse events vs 6.7% receiving placebo. Nonserious drug-related adverse events occurred in 16.9% of zilebesiran-treated patients (principally injection site reactions and mild hyperkalemia) and 8.0% of placebo-treated patients.
Conclusions and relevance: In adults with mild to moderate hypertension, treatment with zilebesiran across a range of doses at 3-month or 6-month intervals significantly reduced 24-hour mean ambulatory SBP at month 3.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04936035.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
RNA Injection Every 6 Months to Improve Adherence and Lower Blood Pressure in Patients With Hypertension.JAMA. 2024 Mar 5;331(9):733-735. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.26071. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38363578 No abstract available.
References
-
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration . Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: a comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(8):634-647. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70102-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Hypertension. Published March 16, 2023. Accessed December 20, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

