MecVax supplemented with CFA MEFA-II induces functional antibodies against 12 adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21) and 2 toxins (STa, LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)
- PMID: 38364078
- PMCID: PMC10986561
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.04153-23
MecVax supplemented with CFA MEFA-II induces functional antibodies against 12 adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21) and 2 toxins (STa, LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)
Abstract
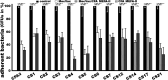
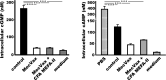
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strains that produce various adhesins and one or two enterotoxins are the leading causes of children's diarrhea and travelers' diarrhea. MecVax, a multivalent ETEC vaccine candidate, consists of two proteins, an adhesin multiepitope fusion antigen (MEFA) that stimulates antibodies to the seven most important ETEC adhesins (CFA/I and CS1-CS6) and a toxoid fusion antigen which stimulates antibodies against ETEC enterotoxins (heat-labile toxin and heat-stable toxin). CFA MEFA-II, another polyvalent MEFA protein, has been demonstrated to stimulate antibodies to another five important ETEC adhesins (CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21). We hypothesize that MecVax coverage and efficacy can be expanded if MecVax could stimulate antibodies to all 12 adhesins. In this study, we supplemented MecVax with CFA MEFA-II, examined broad immunity to the 12 targeted ETEC adhesins and 2 ETEC toxins (STa, LT) in mice, and assessed mouse antibody functions for inhibiting the adherence of the 12 adhesins and neutralizing the enterotoxicity of 2 toxins, thus assessing the potential application of a broadly protective pan-ETEC vaccine. Mice intramuscularly immunized with MecVax and CFA MEFA-II developed robust antibody responses to the 12 ETEC adhesins and 2 toxins; furthermore, mouse serum antibodies showed functional activities against the adherence from each of the targeted adhesins and the enterotoxicity of either toxin. Data also indicated that CFA MEFA-II was antigenically compatible with MecVax. These results demonstrated that the inclusion of CFA MEFA-II further expands MecVax broad immunogenicity and protection coverage, suggesting the feasibility of developing a vaccine against all important diarrheal ETEC strains.IMPORTANCEThere are no vaccines licensed for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), a leading cause of children's diarrhea and the most common cause of travelers' diarrhea. Since ETEC strains produce over 25 adhesins and 2 distinctive enterotoxins, heterogeneity is a key obstacle to vaccine development. MecVax, a multivalent ETEC vaccine candidate, induces protective antibodies against the seven most important adhesins (CFA/I and CS1-CS6) associated with two-thirds of ETEC clinical cases. However, ETEC prevalence shifts chronically and geographically, and other adhesins are also associated with clinical cases. MecVax would become a pan-ETEC vaccine if it also protects against the remaining important adhesins. This study demonstrated that MecVax supplemented with adhesin protein CFA MEFA-II induces functional antibodies against 12 important ETEC adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21), enabling the development of a more broadly protective ETEC vaccine and further validating the application of the MEFA vaccinology platform for multivalent vaccine development.
Keywords: CFA MEFA-II; ETEC (enterotoxigenic E. coli); MecVax; diarrhea; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The senior authors are the inventors of MecVax and are continuously working on the research and development of this ETEC vaccine candidate.
Figures
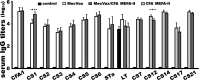
Similar articles
-
Polyvalent Protein Adhesin MEFA-II Induces Functional Antibodies against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Adhesins CS7, CS12, CS14, CS17, and CS21 and Heat-Stable Toxin (STa).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jun 28;89(6):e0068323. doi: 10.1128/aem.00683-23. Epub 2023 May 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37212687 Free PMC article.
-
Intradermally Administered Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Candidate MecVax Induces Functional Serum Immunoglobulin G Antibodies against Seven Adhesins (CFA/I and CS1 through CS6) and Both Toxins (STa and LT).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Feb 22;88(4):e0213921. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02139-21. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34936832 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Characterization of Immunogenicity and Efficacy against Diarrhea from MecVax, a Multivalent Enterotoxigenic E. coli Vaccine Candidate.Infect Immun. 2021 Jun 16;89(7):e0010621. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00106-21. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33875477 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress in Developing Subunit Vaccines against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Associated Diarrhea.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Sep;22(9):983-91. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00224-15. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26135975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress and hurdles in the development of vaccines against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 Jun;11(6):677-94. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.37. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 22873126 Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced intestinal mucosal barrier function damage in a piglet model by modulation of the intestinal microbiome.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 14;11:1494348. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1494348. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39877539 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine alleviates ETEC-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress damage by optimizing intestinal microbial composition in a weaned piglet model.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 16;15:1460127. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1460127. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39351242 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable peptide toxin with 8-arm PEG enhances immunogenicity.J Pept Sci. 2025 Jan;31(1):e3647. doi: 10.1002/psc.3647. Epub 2024 Aug 1. J Pept Sci. 2025. PMID: 39091086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotloff KL, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Nataro JP, Farag TH, van Eijk A, Adegbola RA, Alonso PL, Breiman RF, Faruque ASG, Saha D, Sow SO, Sur D, Zaidi AKM, Biswas K, Panchalingam S, Clemens JD, Cohen D, Glass RI, Mintz ED, Sommerfelt H, Levine MM. 2012. The global enteric multicenter study (GEMS) of diarrheal disease in infants and young children in developing countries: epidemiologic and clinical methods of the case/control study. Clin Infect Dis 55:S232–S245. doi:10.1093/cid/cis753 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Platts-Mills JA, Babji S, Bodhidatta L, Gratz J, Haque R, Havt A, McCormick BJ, McGrath M, Olortegui MP, Samie A, et al. . 2015. Pathogen-specific burdens of community diarrhoea in developing countries: a multisite birth cohort study (MAL-ED). Lancet Glob Health 3:e564–e575. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00151-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . 2018. Global health estimates 2016: deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000 - 2016
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

