Critical role of growth medium for detecting drug interactions in Gram-negative bacteria that model in vivo responses
- PMID: 38364199
- PMCID: PMC10936441
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00159-24
Critical role of growth medium for detecting drug interactions in Gram-negative bacteria that model in vivo responses
Abstract
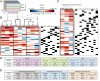
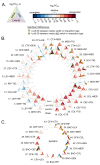
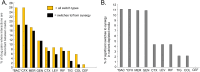
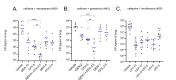
The rise in infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria has necessitated a variety of clinical approaches, including the use of antibiotic combinations. Here, we tested the hypothesis that drug-drug interactions vary in different media, and determined which in vitro models best predict drug interactions in the lungs. We systematically studied pair-wise antibiotic interactions in three different media, CAMHB, (a rich lab medium standard for antibiotic susceptibility testing), a urine mimetic medium (UMM), and a minimal medium of M9 salts supplemented with glucose and iron (M9Glu) with three Gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens, Acinetobacter baumannii (Ab), Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pa). There were pronounced differences in responses to antibiotic combinations between the three bacterial species grown in the same medium. However, within species, PaO1 responded to drug combinations similarly when grown in all three different media, whereas Ab17978 and other Ab clinical isolates responded similarly when grown in CAMHB and M9Glu medium. By contrast, drug interactions in Kp43816, and other Kp clinical isolates poorly correlated across different media. To assess whether any of these media were predictive of antibiotic interactions against Kp in the lungs of mice, we tested three antibiotic combination pairs. In vitro measurements in M9Glu, but not rich medium or UMM, predicted in vivo outcomes. This work demonstrates that antibiotic interactions are highly variable across three Gram-negative pathogens and highlights the importance of growth medium by showing a superior correlation between in vitro interactions in a minimal growth medium and in vivo outcomes.
Importance: Drug-resistant bacterial infections are a growing concern and have only continued to increase during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Though not routinely used for Gram-negative bacteria, drug combinations are sometimes used for serious infections and may become more widely used as the prevalence of extremely drug-resistant organisms increases. To date, reliable methods are not available for identifying beneficial drug combinations for a particular infection. Our study shows variability across strains in how drug interactions are impacted by growth conditions. It also demonstrates that testing drug combinations in tissue-relevant growth conditions for some strains better models what happens during infection and may better inform combination therapy selection.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; Klebsiella; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibiotic resistance; combination therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Khurana S, Singh P, Sharad N, Kiro VV, Rastogi N, Lathwal A, Malhotra R, Trikha A, Mathur P. 2021. Profile of co-infections & secondary infections in COVID-19 patients at a dedicated COVID-19 facility of a tertiary care Indian hospital: implication on antimicrobial resistance. Indian J Med Microbiol 39:147–153. doi:10.1016/j.ijmmb.2020.10.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agyeman AA, Bergen PJ, Rao GG, Nation RL, Landersdorfer CB. 2020. A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment outcomes following antibiotic therapy among patients with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:105833. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.10.014 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
